Aldehyde warehouse that budova. Physical and chemical powers of aldehydes and ketones. Nomenclature and Isomeriya
The first group of authorities is the reactions of advent. In the carbonyl group, between coal and sour, there is an underlying link, which, as you remember, is formed from a sigma-link and a p-link. In reactions, the arrival of pi-links is torn and two sigma links are established - one with coal, the other with sour. On the coals, there is a partial positive charge, on the acid, a partial negative charge. To that, a part of the reagent, anion, is negatively charged to carbon, and a part of the molecule is positively charged to sour.
Perche power - water supply, water supply.
The reaction takes place during heating. Zastosovuєtsya vzhe vіdomy katalіzator gidrovannya - nickel. The aldehydes include the primary alcohols, the ketones the secondary ones.
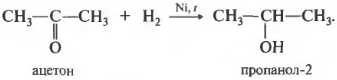
In secondary alcohols, the hydroxogroup is bound from the secondary carbon atom.
friend power - hydration, advent of water. This reaction is only possible for formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. Ketones are called not to react with water.
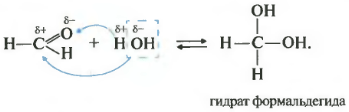
All reactions come in such a way that plus goes to minus, and to plus minus.
As you remember from the video about alcohols, the presence of two hydroxogroups in one atom may not be possible, so speeches are very inconsistent. So the axis of the same two cycles of depression - formaldehyde hydrate and octoic aldehyde - can be, if you want and use only in retail.
The very reactions of the nobility are neobov'yazkovo. Better for everything, nourishment on a dream may sound like a statement of fact, let’s say, with water, that pererakhovanie of speech reacts. In the middle of it, you can use metanal chi etanal.
Third power - the advent of hydrocyanic acid.

Znovu plus go to minus, and minus to plus. There are speeches that are called hydroxintriles. Well, I know, the reaction itself is heard infrequently, but it is necessary to know about power.
quarter power - the arrival of alcohol.
Here, again, it is not necessary to remember the equal reaction, it is simply necessary to understand that such an interaction is possible.

As a rule, in reactions, advancing to a carbonyl group plus to minus, and minus to plus.
P'yate power - reaction with sodium hydrosulfite.

And again, the reaction to dosit is foldable, it’s unlikely that you’ll give up, but it’s one of the akіsnih reactions to aldehydes, so that the sodium force is cut off and falls into a siege. It is the fault of the nobility that the aldehydes react with sodium hydrosulfite, which will be sufficient.
Let's finish with the first group of reactions. Another group is polymerization and polycondensation reactions.
2. Polymerization and polycondensation of aldehydes
We know about the polymerization: polyethylene, butadiene and isoprene rubbers, polyvinyl chloride - the products of the union of impersonal molecules (monomers) into one great, single polymer lane. Tobto, enter one product. When polycondensation occurs, the same, but the polymer also contains low molecular weight products, for example, water. Tobto go out two products.
Otzhe, shoste power - polymerization. Ketones and reactions do not enter, the meaning of the word is only polymerization of formaldehyde.
The pi-link is torn and two sigma bonds are formed with the sucid monomers. Exit polyformaldehyde, titles of paraforms. Nayimovіrnіshe, nutrition on іspitі can sound like this: polymerization reactions enter speech. І a list of speeches has been made, among which there may be formaldehyde.
Soma power - polycondensation. Once again: when polycondensation, cream polymer, go out more low molecular weight, for example, water. Formaldehyde is involved in such a reaction with phenol. For the sake of clarity, we will write down the equalization of the two by phenol molecules.
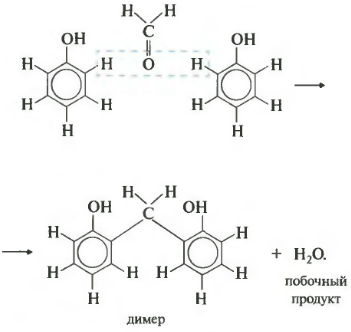
As a result, such a dimer emerges and a water molecule splits. Now let's write down the equal reaction of the infamous looker.

The polycondensation product is phenol-formaldehyde resin. There is a wide range of applications - types of adhesives and lacquers to plastic components of particle boards.
Now the third group of powers is oxidation reactions.
3. Oxidation of aldehydes and ketones
eighth reaction in the first list is a similar reaction to the aldehyde group - oxidation by ammonium oxide to srible oxide. The reaction of a silver mirror. I will say once again, ketones do not enter into this reaction, only aldehydes.

The aldehyde group is oxidized to a carboxyl, acidic group, but in the presence of ammonia, which is the base, a neutralization reaction is immediately observed and ammonium acetate is released. It fell into a siege, twisting the test tube in the middle and creating a mirror surface. Tsya reaction zustrichaetsya on ЄDI postіyno.
Before speech, this reaction is sour on other speech, which can contain an aldehyde group, for example, on formic acid and її salts, and also on glucose.
Dev'yata reaction tezh yakіsna on the aldehyde group - oxidation with freshly precipitated hydroxide midi two. Here I also respect that ketones do not enter into this reaction.

Visually, one can watch the beginning of a yellow siege, which then becomes a chervonim. In some assistants, there is information that the hydroxide midi one is more or less settled, it has a yellow color, which then breaks down into black oxide midi one and water. So the axis is wrong - for the rest of the tribute in the process of falling the siege, the expansion of the particles of oxide midi is changed, as if it is possible to reach the expansions that have been turned into a red color. The aldehyde is oxidized to a double carboxylic acid. The reaction to yoga is very common.
Tenth reaction - oxidation of aldehydes by acidification of potassium permanganate during heating.
Vіdbuvaєtsya znebarvlennya rozchinu. The aldehyde group is oxidized to carboxyl, so that the aldehyde is oxidized to a hydrous acid. For ketones, the reaction does not have any practical sense, but the ruination of the molecule is observed, and the result is a sum of products.
It is important to note that murashiny aldehyde, formaldehyde, oxidizes to carbon dioxide, because murashinic acid is not resistant to strong oxidizing agents.
To pass through the war coal from the stage of oxidation 0 stages of oxidation +4. I guess that methanol, as a rule, in such minds is oxidized to the maximum to CO 2, skipping the stage and aldehyde, and acid. Tsyu sooblivіst slid memorize.
Eleven the reaction is a mountain, an outer oxidation. I aldehydes, and ketones burn to carbon dioxide and water.
Let's write down the equal reaction of the infamous looking.
Behind the law of conservation, masses of atoms are evil, but they can be styled, how many atoms are right-handed. Aje in chemical reactions, the atoms do not go anywhere, but simply change the order of the bonds between them. So the axis of carbon dioxide molecules will be stilki zh, skіlki і atoms of carbon in the molecules of the carbonyl chain, the shards to the warehouse of the molecule include one atom of carbon. So there are n CO2 molecules. Molecules of water will be two times less, lower atoms of water, so 2n / 2, then just n.
Atomіv kisnyu lіvoruch i pravoruch the same kіlkіst. On the right, їх 2n from carbon dioxide, so in the skin molecule there are two oxygen atoms, plus n water, at a time 3n. Livoruch atomіv kisnyu stіlki w - 3n, but one of the atoms is found in the molecule aldehyde, which means that it needs to be seen as a big number, so that the number of atoms should be taken away, so that they fall on the molecular kisen. 3n-1 atoms enter to replace the molecular acid, and therefore there are 2 times fewer molecules, so 2 atoms enter the warehouse of one molecule. Tobto (3n-1)/2 sour molecules.
In this rank, we laid down the fire of carbonic shells at the savage look.
I for example, twelve the power that comes to the reactions of substitution - halogenation by alpha carbon atom. Once again, we're going to get the molecule of the aldehyde. Oxide exerts an electronic charge on itself, creating a partial positive charge on the carbon. The methyl group is magnetized to compensate for the positive charge, moving to a new electron in the water with a lancet sigma star. The sound of coal-water becomes more polar and water is easier to breathe under the hour of attack with a reagent. Such an effect is only possible for the alpha atom of the carbon, because the atom that follows the aldehyde group is independent of the carbohydrate radical.
In this rank, you can take away, for example, 2-chloroacetaldehyde. It is possible to replace atoms in water to trichloroethane further away.
Before the class of oxo compounds, there are organic speeches that avenge the group >C=O, I call it a carbonyl group or carbonyl.
Since the two valences of the carbon atom are occupied by alkyl radicals, the oxo hemispheres are called ketones:
Since the two valences of the carbon atom and carbonyl are occupied by an alkyl radical and a water atom, the oxo hemispheres are called aldehydes.
Ketones and aldehydes are also called carbonyl compounds.
The reactions of aldehydes and ketones are similar, which allows them to be seen in the common class of oxo compounds. The general formula of the homologous series of the largest widths of boundary aliphatic aldehydes and ketones is the same: Z n H 2p.
1. Nomenclature
a) The trivial names of aldehydes are more broad, the stench is associated with trivial names of acids with the same carbonaceous skeleton, it is easy to transform into aldehydes when oxidized: formic aldehyde (formaldehyde), acetaldehyde (acetaldehyde), propion.
According to the IUPAC nomenclature, the presence of an aldehyde group is indicated by a suffix -al(-al):

Since the aldehyde group is not included in the head lances through the presence of older groups, it is indicated by a prefix forms:

b) The names of simple ketones are added up with the names of radicals associated with a carbonyl group, that words ketone:

For the names of folding ketones vicorist, use the suffix -Win(IUPAC):

For the presence of the older group, the ketone group is indicated by the prefix oxo-:

2. Physical power
In a molecule, be it an aldehyde or a ketone, the link with the greater electronegativity of the acid atom is equal to the carbon atom, the decaying electrons and the π-link in the group >C=0 are connected with the acid atom. The reason for this is the appearance of a superfluous electron gap on the carbon atoms (δ-) and a significant change in the electron gap on the carbonyl atom of carbon (δ+), which causes the shift of σ-electron carbon in carbon atoms:

In this order, aldehydes and ketones are polar speech with an overworld electronic shield on the acid atom. Practically all chemical reactions of oxo compounds are bound by such a distribution of electron density in the molecule.
Lower link С=0 є one hour and more reactionary and more mіtsnoy, lower link С=С. So, the energy of the C=O bond is more than 750 kJ/mol, which is much higher, the lower energy of the C-O bond is 360 2 = 720 kJ/mol. A number of zv'yazkiv Z=Z і Z-Z zvorotne spіvvіdnoshennia. The energy of the C=C bond (612 kJ/mol) is slightly less, the lower energy of the C-C bond is lower (339 2 = 678 kJ/mol). The increased reaction of the C=O bond in the polarity of C=Z differs in the electronegativity of the Pro and C atoms.
The shards of molecules of aldehydes and ketones on alcohols and many unsustainable atoms in water, their molecules are not associated and the boiling point of theirs is significantly lower, lower in alcohols. Zagalom is the boiling point of ketones of trohi vischa, lower isomeric ones of aldehydes. Razgaluzhennya lansyuga viklikaє regular decrease in temperature of boiling. The lower members are low - acetone, formaldehyde, acetaldehyd - retail in drinking water, other aldehydes and ketones are more important than the largest organic retailers (alcohol, ether thin.). Lower aldehydes have a pungent odor, aldehydes 3 -3 6 have an unacceptable odor, higher aldehydes have floral odors and tend to get stuck in perfumery.
Aldehydes and their chemical powers
Aldehydes are such organic speech, in the molecules of which the carbonyl group is bound, at least, with one atom of water and carbohydrate radical.
The chemical power of aldehydes is determined by the presence of the carbonyl group in the molecule. The linkage with cym at the molecule of the carbonyl group can be indicative of an adventitious reaction.
So, for example, if you take and skip a bet of formaldehyde at once with water over a heated nickel catalyst, then adding water and formaldehyde will turn into methyl alcohol. Krіm tsgogo, the polar character of the tsy zv'yazku spawns and such a reaction of aldehydes, like the advent of water.
And now let's look at all the features of the reactions in the form of water. The next step is to add a hydroxyl group to the carbonyl atom of the carbonyl group, which carries a partial positive charge, the electron vapor of the acid atom.

With such an adventitious characteristic offensive reaction:
First, hydrogenation is carried out and the primary alcohol RCH2OH is dissolved.
In a different way, it is necessary to add alcohols and to dissolve the alcohols R-CH (OH) - OR. And in the presence of chlorine water HCl, which acts as a catalyst, and with excess alcohol, it is possible to dissolve acetal RCH (OR) 2;
Thirdly, it is necessary to add NaHSO3 to sodium hydrosulfite and dissolve similar hydrosulfite aldehydes. When aldehydes are oxidized, such special reactions can be observed, such as interactions with ammonium oxide sribl (I) and with midi (II) hydroxide and the elimination of carboxylic acids.
During the polymerization of aldehydes, such special reactions are characteristic, as linear and cyclic polymerization.
How to talk about the chemical power of aldehydes, next to guess the oxidation reaction. Before such reactions, one can add the reaction of the silver dzerkala and the reaction of the svetlofor.
You can watch for the unusual reaction of the siberian dzerkala by checking in the class with a cicavius dosvid. For which you need a pure vimite test tube, pour a small amount of ammonium oxide into the glass, and then add some chotiri or five drops of formalin. At the next stage, when carrying out the test, it is necessary to place the test tube in a flask with hot water, and at the same time you will be able to make it look like a sparkling ball appears on the walls of the test tube. Tse pokrittya є siege metal srіbl.

And the axis is called the “svetlofor” reaction:

Physical power of aldehydes
Now let's get down to looking at the physical powers of aldehydes. How can the powers that be be able to speak? Pay close attention to those that a number of simple aldehydes are a barless gas, folded representations in the sight of the motherland, and the axis of the main aldehydes is the hardness of speech. The greater the molecular weight of aldehydes, the greater the boiling point. So, for example, propionic aldehyde reaches the boiling point at 488 degrees, and the axis of propyl alcohol boils at 978 0C.
If you talk about the abundance of aldehydes, then it's less for one. So, for example, ostovy and murashiny aldehydes may be powerless to vary by the water, and folded aldehydes may weaken building to rozchinennya.
Aldehydes, which can be seen to the lowest level, have a sharp and unacceptable smell, and solids that are indistinct in water, on the other hand, are characterized by a pleasant floral smell.
Knowledge of aldehydes in nature
In nature, representatives of various groups of aldehydes appear everywhere. The stench is present in the green parts of the roslins. This is one of the simplest groups of aldehydes, to which the formic aldehyde CH2O can be found.
Aldehydes are also processed with a folded warehouse. Before such views lie vanilin and grape tsukor.
However, since aldehydes can easily enter into all sorts of interactions, they can succumb to oxidation and renewal, then we can say with confidence that aldehydes are even more mature to rare reactions, and that in pure looking stench is more pronounced. And the axis of their pokhіdnі can be seen everywhere, like in a growing middle, so are creatures.

Stasis of aldehydes
Aldehydna group is present in many low natural speeches. Їx characteristic rice, take bagats from them, є smell. So, for example, the representatives of the higher aldehydes, are filled with different aromas and enter the warehouse of ethereal oils. Well, as you already know, such olis are present in flowery, spicy and spicy roses, fruits and fruits. The stinks knew the scale of the selection of handicrafts and the selection of perfumes.
Aliphatic aldehyde CH3(CH2)7C(H)=Pro can be found in essential citrus oils. So aldehydes can smell of orange, and stagnate in the food industry, like a flavoring agent, as well as in cosmetics, perfumery and butovy chemistry, like a perfume.
Murashiny aldehyde is a non-barrel gas, which may have a sharp specific smell that is easily dispersed in water. Such an aqueous solution of formaldehyde is also called formalin. Formaldehyde is more toxic, but in medicine it stagnates in a grown-up looking like a disinfectant zasib. Yogo vikoristovuyut for disinfection of tools, and yogo weak rozchiny vikorivuyut for washing the skins for strong drinkability.
In addition, formaldehyde vicarious with tanned shkir, so that the building can be covered with white tongues, like in the warehouse shkir.
In the agricultural state, formaldehyde miraculously proved itself to be an hour of grain harvesting before the last robots. Yogo zastosovuyut for the production of plastics, as it is so necessary for the technique and buttock needs.
Ost aldehyde is a barren homeland, as it has the smell of sweet apples and is easily dispersed by the water. Zastosovuєtsya wines for the removal of ocular acid and other speeches. Ale shards of wine with brittle speech, then it can vibrate the destruction of the body, or the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes and wild paths.
5.1. Zagalna characteristic
Controversial classes of aldehydes and ketones should replace the functional carbonyl group and be considered up to carbonyl spoluk. For them, the name is also victorious oxospolki, oskіlki group \u003d O is called an oxo group.
Aldehydes are called half-shells, in which the carbonyl group is attached to an organic radical and a water atom; ketones - carbonyl halfs with two organic radicals.
The group -CH=O, which enters the warehouse of aldehydes, is called aldehyde, vidpovidno group in ketones - ketone, or ketogroup.
Fallow due to the nature of organic radicals aldehydes and ketones can lie up to aliphatic or aromatic row; ketoni buvayut zmіshanimi(Table 5.1).

Aldehydes and ketones have daily interactions with atoms of sour rukhli and water on the surface of alcohols. In the bond with cym aldehydes and ketones, they are not associated with the water-soluble bonds, but rather less until the water bonds are dissolved with water molecules, and to that good they are separated in it (especially the first members of the homologous series).
Table 5.1.Aldehydes and ketones

5.2. Reaction centers for aldehydes and ketones
sp 2 -Hybridization of the carbon atom of the carbonyl group makes three σ-bonds, which lie in the same plane, and π-bonds with the atom sour for the rahunok of the unhybridized p-orbital. As a result, the electronegativity of the carbon atoms and the acidity of the π-bonds between them is strongly polarized (Fig. 5.1). In the result, carbon atoms of the carbonyl group have a partial positive charge δ+, and in the acid atoms, a partial negative charge δ-. Oskilki atom of carbon is electron-deficient, wine is the center for nucleophilic attack.
Rozpodil electronic power in the molecules of aldehydes and ketones with the improvement of the transfer of electronic injection of electronic

Rice. 5.1.Electronic Budova carbonyl group
the deficient carbon atom of the carbonyl group from σ-links is shown in Scheme 5.1.
Scheme 5.1.Reaction centers in the molecules of aldehydes and ketones

Molecules of aldehydes and ketones have a few reaction centers:
The electrolytic center - the carbon atom of the carbonyl group - signifies the possibility of a nucleophilic attack;
The main center - the acid atom - makes it possible to attack with a proton;
CH-acid center, an atom of water, which may have a weak proton friability, and may, zocrema, be attacked by a strong base.
In general, aldehydes and ketones may be highly reactive.
5.3. Nucleophilic advent
For aldehydes and ketones, the reactions of nucleophilic addition are most characteristic. A N.
Full description of the mechanism of nucleophilic adsorption A N
The ease of nucleophilic attack on the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of the aldehyde or ketone is determined by the value of the partial.
positive charge on the atoms of carbon, yogo openness and acid-base powers of the medium.

Due to the elimination of the electronic effects of groups bound to the carbonyl atom of carbon, the value of the partial positive charge δ+ per nth in aldehydes and ketones changes in the next row:

The space availability of the carbonyl carbon atom changes when water is replaced by more bulk organic radicals, so aldehydes are more reactive, less ketones.

General scheme of nucleophilic addition reactions A N to the carbonyl group, it includes a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl atom of the carbon, followed by the addition of an electrotrophil to the acid atom.

In an acidic medium, the activity of the carbonyl group, as a rule, increases, the shards after the protonation of the acid atom on the carbon atom cause a positive charge. Acid catalysis of vicorous sounds only if the attacking nucleophile has low activity.
Behind the induction mechanism, a number of important reactions of aldehydes and ketones take place.
A lot of power in aldehydes and ketone reactions occur in the minds of the body, and the reactions are presented in the forward sections of the handkerchief. In this division, the most important reactions of aldehydes and ketones will be considered, as shown in Scheme 5.2 at a glance.

Admission of alcohol. Alcohols, when interacting with aldehydes, are easily dissolved napivecetal. Napіvacetals do not sound through their incompatibility. When there is too much alcohol in the acidic medium, the napivecetals are transformed into acetals.

The stagnation of the acid catalyst during the conversion of the acetal to the acetal becomes clear from the reaction mechanism induced below. The central place in the new loan is the adoption of the carbocation (I), stabilized for the part of the unshared electron pair in the acid atom (+ M-effect of the C2H5O group).

Reactions of the conversion of napivecetals and acetals were metabolites, so acetals and napivecetals are easily hydrolyzed in excess of water in the acidic medium. In the puddle medium, napivecetal stalk, as the alkoxidion is the most important group, the lower hydroxide-ion.
The solutions of acetals often vicorist as timchasovy zahist of the aldehyde group.
Come drive. Bring it to the carbonyl group - hydration- reverse reaction. Steps of hydration of aldehyde or ketone in water distribution should be deposited in the substrate.
The product of hydration, as a rule, is not visible for additional distillation, the shards of wine are laid out on the outer components. Formaldehyde in aqueous hydration is more low by 99.9%, acetaldehyde is about half, acetone is practically not hydrated.

Formaldehyde (murashiny aldehyde) may cause protein digestion. Yogo 40% water ranks, ranks formalin, zastosovuetsya in medicine as a disinfectant zasib and preservative of anatomical preparations.
Trichloroacetic aldehyde (chloral) hydrated in full. The electron-withdrawing trichloromethyl group of the flooring stabilizes chloral hydrate, which makes the crystalline speech water only during distillation in the presence of dehydrating speeches - sulfuric acid and other.

In the basis of the pharmacological effect of CC1 chloral hydrate s CH (VIN) 2 lie a specific injection on the body of the aldehyde group, which is mindful of the disinfecting power. Atoms of the halogen help to reduce the toxicity of the speech, and the hydration of the carbonyl group reduces the toxicity of the speech by burning.
The advent of aminos and their dead ones. Aminos and other nitrogenous compounds from the seminal formula NH 2 X (X = R, NHR) react with aldehydes and ketones in two steps. The products of the nucleophilic admixture are digested on the back, and then, due to the instability, they release water. In connection with this process, they classify it as a reaction. arrival-disconnection.

Different primary aminos have substitutions name(they are also called Schiff's substations).
Imeni - intermediate products of rich enzymatic processes. Otrimannya iminiv to pass through the stage of amino alcohols tasting, as if they become effective, for example, when formaldehyde interacts with α-amino acids (Div. 12.1.4).
Іmini є by industrial products the possession of amines with aldehydes and ketones in a way dnovlyuvalnogo amіnuvannya. This ardent method is based on the innovation of the sum of the carbonyl compound with ammonia (or amine). The process proceeds according to the scheme of advent-split from the approval of the imin, which is confirmed in the amin.
When aldehydes and ketones interact with similar hydrazine, hydrazone. This reaction can be victorious for seeing aldehydes and ketones with sums and chromatographic identification.

Substantiate Schiff and other similar varieties are easily hydrolyzed by water grades of mineral acids from the base of outdoor products.
Most often for the reactions of aldehydes and ketones with nitrogenous bases, acid catalysis is required, which will speed up the dehydration of the product. However, if you increase the acidity of the medium too early, then the reaction will occur as a result of the conversion of the nitrogenous base to the non-reactive acid XNH 3+.
Polymerization reaction. The reaction of power is more important than aldehydes. When heated from mineral acids, polymers of aldehydes disintegrate into the products.
The solution of polymers is possible as a result of nucleophilic attack by the acid atom of one molecule of the carbonyl aldehyde atom on the other molecule. So, when formalin is standing, it falls off in a white precipitation of the polymer formaldehyde - paraform.
5.4. Condensation reactions
The presence of the CH-acid center in the molecule of the aldehyde or ketone should be brought to the point where the α-atoms of the water of these carbonyl halfs can cause proton friability to the deuce. Under the principle of such protons, protons can be added to the approved carbanions. Carbanions play the role of nucleophiles in relation to the carbonyl substrate. The reason is the possibility of reactions, in which one molecule, like a nucleophile, joins to the carbonyl group of another molecule of a neutral carbonyl unit. Such processes can be seen before the condensation reaction.
Condensation is called a reaction, which leads to the formation of a new carbon-carbon coal bond, moreover, for two or more apparently simple molecules, a new, collapsing molecule is established.
So, in the puddle medium, two molecules of acetaldehyde are dissolved hydroxialdehyde with a double number of carbon atoms.
The product of the reaction, which replaces the hydroxyl and aldehyde groups, is called aldol(incl. lines ald egid that alcohol ol), and the reaction itself was named aldol condensation, or aldol advent.
The mechanism of aldol condensation. When dividing the base in the carbonyl site, a proton from the α-position is split and the carbanion (I) is dissolved, in which the negative charge is delocalized through the participation of the carbonyl group.

Anion (I) is a strong nucleophile (at the advanced stage of the mechanism of color indications), which joins another (unionized) carbonyl molecule. As a result of this interaction, a new C-C bond is formed and intermediate alkoxide ion (II) is dissolved. In an aqueous medium, the anion stabilizes, splitting a proton into a water molecule, and transforming into a terminal product - an aldol.

The reaction of aldol addition is shown on the example of propanal (the molecule is seen in color, which joins the C=Pro group of the other molecule); a similar reaction was induced with the butt of acetone.

The product of condensation - aldol - building up to the splitting of water with solutions of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound. Zvuchay tse v_dbuvaєtsya for podvischenoї temperature. And here the reaction is called a fire croton condensation.
Condensation reactions can proceed in a different variant, with different carbonyl halfs, moreover, one of them may not avenge the CH-acid center, like, for example, formaldehyde and benzaldehyde in offensive reactions:

Aldol condensation - reverse reaction; the reverse process is called aldolni splits(or retroaldol reaction). Offensive reactions occur in many biochemical processes.
5.5. Reinforcement and oxidation
Reinventionaldehydes and ketones are used for additional complex metal hydrides LiAlH 4 , NaBH 4 . The reaction includes a nucleophilic attack of the carbonyl atom with carbon hydride-ion.
With a slight hydrolysis of alcohol, having settled, the first or second alcohol comes out.

Oxidationaldehydes in carboxylic acids are affected by a greater number of oxidizing agents, including sour. Ketones in soft minds do not oxidize.

Oxide srіbla like an amino complex 2 OH (Tollens' reagent) oxidizes aldehydes in carboxylic acids, metal srіblo is seen in its own. Sounds like a name - reaction "Siberian mirror".
Also, aldehydes are easily oxidized by midi(II) hydroxide in the puddle medium.
Offensive reactions are often vicorous as if they were for the manifestation of the aldehyde group, although odors are nonspecific in relation to aldehydes: oxidation with significant reagents, for example, rich atomic phenols, aminophenols, aromatic amines, hydroxide ketones and easily oxidized with.
1. Aldehydes and ketones: budova, isomeria, nomenclature. Chemical power. Basicity. Reactions of nucleophilic admixture. Revision to alcohols and carbohydrates. Reactions of aromatic aldehydes and ketones for the participation of the aromatic nucleus.
Aldehydes and ketones are present up to carbonyl organic collections.
Carbonyl halfs are called organic speech, in molecules of which there is a C=O group (carbonyl or oxogroup).
The general formula of carbonyl sprouts:
Functional group -CH \u003d Pro is called aldehyde.
Ketoni- organic speech, the molecules of which replace the carbonyl group, obtained from two carbohydrate radicals. Global formulas: R 2 C \u003d O, R - CO - R ' or
Star C=Pro is strongly polar. Її the dipole moment (2.6-2.8D) is significantly higher, lower in the С–О bond in alcohols (0.70D). Electrons that are a multiple of the C=O bond, especially the most destructive p-electrons, are shifted to an electronegative atom of sourness, which leads to the appearance of a new partial negative charge. Carbonyl carbon is charged with a partial positive charge.
That is why coal is attacked by nucleophilic reagents, and oxyfuel - by electrochemical ones, including H +.
Molecules of aldehydes and ketones have daily atoms and water, which last until the water bonds dissolve. That is why the boiling point is lower, lower in alcoholic spirits. Methanal (formaldehyde) - gas, aldehydes C 2 -C 5 and ketones C 3 -C 4 - rіdini, vischi - hard speech. Lower homologues are different in water, water-soluble bonds are formed between water molecules, water molecules and carbonic acid atoms. With the increase in the carbohydrate radical, the versatility of the water decreases.
Systematic names aldehydes I will be after the name of the vodpovidny carbohydrate and the addition of the suffix -al. The numbering of the lancet is started from the carbonyl atom of the carbon. Trivial names are vibrated in the form of trivial names of these acids, as aldehydes are transformed during oxidation.
Systematic names ketones incoherently vibrating in the name of radicals (in order of increase) with the addition of the word ketone. For example:
CH 3 -CO-CH 3 - dimethyl ketone(Acetone);
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 -CO-CH 3 - methylpropyl ketone.
In the wild type, the name of the ketone will be followed by the name of the type of carbohydrate and the suffix -Win; The numbering of the lancet is started from the rank of the lancet closest to the carbonyl group (IUPAC replacement nomenclature).
Apply:
CH 3 -CO-CH 3 - propane wine(Acetone);
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 -CO-CH 3 - pentane wine- 2;
CH 2 \u003d CH-CH 2 -CO-CH 3 - pentene-4 - wine- 2.
Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones.
Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by structural isomerism.
Isomerism aldehydes:
interclass isomerism (similar to aldehyde).
Reactions of nucleophilic admixture.
Aldehydes and ketones are easy to add nucleophilic reagents C=Pro link. The process begins with the attack of the nucleophile on the carbonyl carbon atom. Let's take a tetrahedral intermediate, which is settled at the first stage, adding a proton and giving the product:
The activity of carbonyl compounds in Ad N-reactions (reactions of nucleophilic addition) depends on the magnitude of the effective positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom and the dependence of the substitutes on the carbonyl group. Electron-donor and volume intercessors facilitate the reaction, electron-acceptor intercessors promote the reaction building of the carbon plant. Therefore, aldehydes in Ad N-reactions are active, lower ketones.
Admission of alcohols and thiols.
Aldehydes add alcohol to the decisions drink acetals. With an excess of alcohol and in the presence of an acid catalyst, the reaction went far - until acetals
Do not give ketals for similar minds.
Thiols, as strong nucleophiles, lower alcohols, dissolve the products of admixture with aldehydes and ketones.
Admission of hydrocyanic acid
Hydrocyanic acid rises to the carbonyl half in the minds of the main catalyzes of the dissolved cyangidrins.
Addition of sodium bisulfite.
Aldehyde and methyl ketonium add sodium bisulfite NaHSO 3 with solutions of bisulfite compounds.
Come drive.
Aldehydes and ketones add water to the solutions of hydrates. The reaction proceeds in reverse. Hydrates that settle are not thermodynamically stable. Rivnovagu changed in bik produktіv priednannya less in different active carbonyl slugs.
Reactions of nucleophilic addition of nitrogenous bases.
Before these reactions lie:
a) enlightenment of imine (azomethine) - the basics of Schiff
c) the adoption of hydrazones
d) synthesis of semicarbazones
Revision to alcohols and carbohydrates.
The addition of water to aldehyde molecules is found behind the lower link at the carbonyl group. The product of hydrogenation of aldehydes is primary alcohol, ketones are secondary.

a) inspired by Clemmensen.
As a carbonyl half-stack to di acids, then vicorist this type of renewal
b) renewal according to Kizhner-Wolf
This kind of inspiration is victorious in quiet valleys, if the object of inspiration is stable to the foundations
Ammonia oxidizes the hydroxide of the slab OH when lightly heated with aldehydes (but not ketones) oxidizes it to acid and dissolves the free metal slab. Like a test tube, in a kind of reaction, the bula was frontally sparse in the middle, fell like a thin ball on the inner surface - a silver mirror was settling down:

Ketones do not enter into such reactions. They have a "zhorstke oxidation" - having opened the link C-C
The halogenation reaction. Aldehydes and ketones readily react with halogens to dissolve a-halogenoviruses:

Reactions of aromatic aldehydes and ketones for the participation of the aromatic nucleus.
There are such types of carbonic half arenas.
In the reaction of electrotrophic substitution, aromatic aldehydes enter normally up to the rules of orientation. Aldehydna group - electron-withdrawing group, won't show -I; -M-effects and are brought to metaorientations.
For example:

Nitrogenation of acetophenone is easy to overcome by an irritating mixture at a temperature of 0 0 С:
m-nitroacetophenone
2. Carbohydrates. Classification and nomenclature. Budov, configuration and conformation.









In living nature, carbohydrates have the following functions:
– energy supply in metabolic processes (starch in roslins, glycogen in living organisms);
- Structural components of the walls of roslin (cellulose); - win the role of substrates and regulators of specific biochemical processes;
є warehouse elements of life important speeches: nucleic acids, coenzymes, vitamins and other.
- Carbohydrates serve as the main component of zhі ssavtsіv, and people will be taken care of even, clothes and life.
Before carbohydrates, 60-70% of the grub diet is added. The stench is important in growing products, as the main components of bread, cereals, pasta, confectionery products, to serve as syrovin in the fermentation industry, in the production of harchic acids: octoic, lactic, citric.
Tilki roslin zdatnі zdіysnyuvat povny synthesis in carbohydrates in the path of photosynthesis, in the process of which water and carbon dioxide are converted into carbohydrates under the action of sony light like dzherel energy. Creatures of organisms are not capable of synthesizing carbohydrates and take them from the growing gerel:
3. Budova, isomeria, nomenclature of monobasic carboxylic acids. Chemical power. Reactions with nucleophilic reagents. Abatement of acid halides. Reinvention. Decarboxylation reactions. Functional effects of carboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids, nomenclature and authority.

Zagalna formula boundary one. car. acids 





![]()
Carboxylic acids functional travel, up to which one can see acid halides, folded ethers, anhydrides, amides and nitriles of acids. Anhydrides, amides and nitriles without the middle of acids are most often impossible to remove, this is done by indirect methods.



Update:
Carboxylic acids can only be relied upon for the help of even stronger guides. Therefore, with the addition of acids, they do not contain aldehydes, but only primary alcohols.
You can vicorate diborane (BH3) 2 .
Decarboxylation- the elimination of CO2 from carboxylic acids or their salts. Decarboxylation is carried out by means of heating in the presence of acids or bases. At the same time, the substitution of the carboxyl group for the water atom is heard.
Unsubstituted monocarboxylic acids decarboxylate in hard minds.
Decarboxylation is easier for the presence of electron-withdrawing substitutes in the a-position.
Decarboxylation by means of heating (dry distillation) of calcium and barium salts of carboxylic acids - the method of removing ketones.
Dicarboxylic acids. Nomenclature and power
4. Alkeni. Reactions of electrotrophic addition of alkenes (reactions Ade): Markovnikov's rule and explanation. Free-radical intake of halogens and bromine water. Allylene halogenation. Homogeneous and heterogeneous hydrogenation.
Alkenes (olefins). In carbohydrates, which avenge one subvine of charcoal-carbonaceous links, in the case of a single lance, they are called alkenes. Zagalna that gross formula З n Н 2 n . A series, the members of which are divided by (2H) n, are called an isological series. The first representative of CH 2 \u003d CH 2 (ethene - ethylene), sp 2 - hybridization.
Ad E reactions are the main type of alkene transformation. Halogens, hydrogen halides, sulfuric acid, water and other electrochemical reagents can follow the electrochemical mechanism to alkenes.
The main mechanism of the reaction includes a low last stage:
At the first stage, electrotrophil forms a p-complex with an alkene, in which the dependent bond acts as a donor, and electrotrophil acts as an electron acceptor. Further, the p-complex is regularly rearranged into a carbocation (s-complex). At the last stage, the interaction of the carbocation with the nucleophile (Y -) with the approved product is observed.
Alkenes react with bromine and chlorine to dissolve products and add a dependent linkage of one molecule to a halogen with a yield close to acidic. Fluorine is also active and leads to the destruction of alkenes. The advent of iodine to alkenes in most of the cases is reversed by the reverse reaction, which is similar to that of the other reagents.
In reactions involving the addition of polar molecules of the HX type to non-symmetrical alkenes, water is added to a hydrogenated carbon atom with a chain link (that is, a carbon atom connected with the largest number of atoms in water).
Advent against the rules of Markovnikov is assigned to the vipadkah, if the intercessor for the underwire connection is charged with the electronic power of the wines, then. shows electron-acceptor power (– I that/or - M-effect).
For example, in the reaction of trichloropropene Cl 3 C-CH=CH 2 with HX, water rises to a less hydrogenated carbon atom, and X to a more hydrogenated one. This is due to the fact that the СCl 3 group exhibits a negative inductive effect and the p-electronic bond of the С=З bond is shifted to a smaller hydrogenated carbon atom.
In addition, if the reaction comes not for an electrochemical, but for a radical mechanism, then Markovnikov's rule is also not applied. Thus, the reaction of HBr with propylene in the presence of peroxides (H 2 O 2 or R 2 O 2 ), which form free-radical moieties (HO or RO), follows a radical mechanism and goes against Markovnikov's rules.
Allyl substitution with halogens.
CH 2 \u003d CH-CH 3 + Cl 2 ® CH 2 \u003d CH-CH 2 Cl + HCl
Such a direct chlorination of bindings due to the stability of the allyl radical, which is obtained during the implementation of the radical-lanceg process:
Initiation:
Cl 2 + M ® 2Cl + M
Homogeneous and heterogeneous hydrogenation of alkenes.
A line of heterogeneous and homogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. In heterogeneous hydrogenation, finely shaped metal catalysts are present - platinum, palladium, ruthenium, rhodium, osmium and nickel, either in pure appearance, or deposited on an inert nose - BaSO 4 CaCO 3 activated carbon, Al 2 O 3 and so on. organic media and act as heterogeneous catalysts. Ruthenium and rhodium are the most active among them, and platinum and nickel are the most widely used. Platinum sounds like black dioxide PtO 2 widely known under the name "Adams catalyst". Other active metals of the platinum group vicorist on inert wears, for example, Pd/C or Pd/BaSO 4 , Ru/Al 2 O 3 ; Rh/C and in. Palladium, applied to the coal, catalyzes the hydrogenation of alkenes to alkanes in alcohol at 0-20 0 C and normal pressure. The nickel is victorious at the sight of the so-called "Raney's nickel".
The hanging link in alkenes is hydrogenated with a greater degree of hydrogenation with other functional groups (C=O, COOR, CN, etc.) minds (0-20 0 C and with atmospheric pressure).
Heterogeneous hydrogenation on the surface of metal catalysts may contain a number of small fractions, such as the isomerization of alkenes and the splitting of single carbon-carbon bonds (hydrogenolysis). Homogeneous hydrogenation relieved of these nedolіkіv. The shortest homogeneous hydrogenation catalysts are the complexes of rhodium (I) chloride and ruthenium (III) chloride with triphenylphosphine - tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium chloride (Ph 3 P) 3 RhCl (Wilkinson catalyst) and tris(triphenylphosphine) ruthenium hydrochloride (Ph 3H3).
The importance of homogenous catalysts influences the possibility of selective replacement of mono- or both substitutions of sub-links in the presence of three-and tetra-substitutions of sub-links due to the large differences in the presence of double bonds.
5. Alkin. Reactions of alkynes. CH-acidity. Acetylene, budova that dominion. Reactions of electrotrophic and nucleophilic reactions, their mechanisms. Oxidation, redevelopment, hydrogenation of alkynes.
Alkynes (acetylenes). In carbohydrates, which avenge one loss of carbonaceous-carbonaceous linkage, in the case of lanceolates, they are called alkynes or acetylenes. Zahalna is the gross formula З n Н 2 n -2 . The first representative of CHºCH (etin - acetylene).
Similar to alkenes, alkynes are less active in reactions of electrotrophic addition and more active in reactions with nucleophiles, for example, with amines and alcoholates. Tim is not less, alkyne, yak and alkenes, it is easier to react with electrochemical reagents, lower with nucleophilic ones. Greatly in a rush to get spivvіdnoshnja shvidkosty reactions of alkenіv and alkіnіv nadaє nature rozchinnіv.
In the sp-hybridization steel, the carbon atom can have the greatest electrical orientation, so it can lead to a strong C-H acidity terminal acetylene groups. The atom of water, which is found in the presence of a carbonaceous potion bond, has a greater acidity, the lower atom of water is alkenes and alkanes. It is explained by the fact that C atoms attract electrons more strongly, so the C-H bond of polarization and electropositive atoms and water show great acidity in them. The acidity of acetylene and a-alkynium is manifested in the following reactions:
![]()
The amide-anion has a high basicity, which makes it possible for the acetylenide to be more stable. Vodnochas water, volodyuschy acidity pored with acetylene, with the rest of acetylenides: 
Sodium, potassium and other acetylenides of puddle metals and true salts, which are formed from the metal cation and acetylenide anions. Acetylene salts with important metals (Ag, Cu, Hg) - above all rose salts. Tse covalently zbudovani z'ednannya, indistinct near the water. The stinks settle from the water line.
1. hydration. The water rises to a trinary tie at the presence of the silence of the catalysts themselves, which is up to the subway:
2. Halogenation. Admission to chlorine, bromine and iodine to alkynive by electrochemical mechanism, also with less fluidity, lower to alkenive. Trans-dihaloalkenes, which dissolve with cioma, are easily seen, shards are farther away from the halogen (chromium chlorine) going through great difficulties:

3. Hydrohalogenation. The halogen waters are added to alkynes by the electrochemical mechanism. For example, when hydrogen chloride is added to acetylene, chlorovinyl and 1,1-dichloroethane come out sequentially. The advent of halogens and halogens to alkynes can proceed by a radical mechanism. In case of electrostatic approach, Markovnikov's rule is applied, in case of radical mechanism, a direct approach is observed.
4. Hydration. Water is added in the presence of mercury sulfate (Kucherov's reaction), or over heterogeneous catalysts, with which acetylene comes out aldehyde, and with other acetylene carbohydrates - ketones due to regrouping of enols, which dissolve:

5. Admission of alcohols. The advent of alcohols in the presence of alcohols is the reaction of nucleophilia advent. As a result, vinyl ethers and acetals are dissolved:
6. Admission of HCN. Cyanohydric acid adjoins to acetylene in the presence of midi(I) salts, resulting in the dissolution of acrylic acid nitrile (acrylonitrile):
7. Oxidation.


Alkynes are oxidized by potassium permanganate in a neutral medium along the tribal linkage, dissolving carboxylic acids (potassium salts are dissolved in the brains of the reaction):
Acetylene in the urine is oxidized to potassium salt of oxalic acid - potassium oxalate.
8. Education of acetylenides. At the same time, the atoms of the water are replaced by atoms of the metal:
otherwise, for different metals:
9. Substitution of water with halogens. In case of hypohalogenity, water atoms in the potrine linkage can be replaced by halogen atoms:
10. Polymerization. Fallow in the minds of the reaction and the zastosovuvanny kalizator polymerization of acetylene can run through different paths:
dimerization it is used for dilution of ammonium chloride and midi (I) chloride in water, at which butyn-3-en-1 (vinylacetylene) is dissolved:
trimerization proceeds at 500-600 pro 3 in the presence of activated carbon, the reaction product is benzene (Zelinsky reaction):

tetramerization it is used under the influence of complex compounds to nickel, mainly cyclooctatetraen-1,3,5,7 is dissolved:

10. Adoption of magnesium-organic shelves. Mixture of magnesium acetylenide (Jocic's reagent), which is vicorous for various syntheses, reduces the proportion of methylmagnesium iodide to alkine, which contains an atom of water at a loss of binding:
6. Halogenated carbohydrates. Reactions of nucleophilic substitution and splitting. Aromatic halogenated.
To halogen-like carbohydrates, half-halfs can be seen, so that one or more atoms can be replaced by halogen atoms.
Halogenated carbohydrates are classified according to the nature of the carbohydrate radical (aliphatic, ali-cyclic and aromatic), the number of atoms in the halogen in the molecule (mono-, di-, tri- and polyhalogenovirus), the nature of the halogen (fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodine). ), the nature of the carbon atom, with which it binds the atom to the halogen (primary, secondary and tertiary halogenated).
Nomenclature. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, the names of halogenated carbohydrates are added similarly to the names of similar carbohydrates. On the back of the head, indicate the position of the substitution with a number (as it is necessary), then name the halogen (as it is necessary - there are a number of atoms in front of it) and add the name of the parent structure (in aliphatic halogen-like chains, the head carbonaceous lance, in alicyclic and aromatic ones - the cycle).
The numbering is started from the closest to the halogen end of the carbonaceous lance.

1 - bromopropane 1,2 - chlorocyclohexane chlorobenzene
Reactions of nucleophilic substitution
Aromatic halogenated with a halogen in the nucleus (halogenaryl) - to complete the inert speech line with halogen-producing alifatic rows. Therefore, the stench is forced to enter the reaction of nucleophilic substitution. Such inactivity of the halogen atom in halogenaryls is explained by the partial doubling of yogo with the benzene ring:

Tse guess the behavior of halogen-like non-carbohydrates, in which the halogen atom is found with carbon, which is associated with a lower bond. Therefore, for carrying out the reactions of halogenaryls with nucleophilic reagents, you need a quick mind (high temperature and pressure):

Atoms of halogens can be replaced by junk and can be replaced by different nucleophiles, which are victorious for the synthesis of different ones:
Reactions of elimination (disintegration) – dehydrohalogenation
As a result of the elimination reaction, alkenite and hydrogen halide are dissolved in several alkyl halides.
For example, when ethyl chloride is heated in a meadow, alcohol removes HCl and dissolves ethylene:
If you take care that you carry out this reaction in water, and not in alcohol, then the main product will be alcohol, and not an alkene.
In several asymmetric alkyl halide reactions, dehydrohalogenation proceeds normally up to Zaitsev's rule: The splitting of the water atom in the reactions of the splitting of HX resembles the smallest hydrogenated carbon atom.
7. Aromatic halfs (areni). Aromatic character of benzene. Energy of achievement, aromaticity criteria. Reaction of electrotrophic substitution of benzene. Budov π- and σ-complexes. Having poured in the defenders of the benzene ring directly, that quickness of the reactions of electrotrophic substitution.
The main feature of aromatic carbohydrates and equal distribution of π-electron thickening in the molecule. A single rack is a closed system of π-electrons in a cyclic molecule - the main sign of aromaticity. Necessary mental for such right-handedization of π-electrons is the parallelism of the axes of 2p-orbitals, which take part in the illumination of a closed π-electron system. That's why the molecules of aromatic spoluk obov'yazkovo toil the plane of Budov. Even though the mind is not defeated, the circular succession of π-electrons is destroyed. As a result, the floor is not aromatic. Aromatic half-shells are also characterized by a small number of π-electrons in the molecule. German chemist-theorist E. Hückel viviv p r and v l about (1931): flat cyclical half, which can be obtained a system of π-electrons, can be aromatic, so the number of these electrons is 4n + 2 (de p \u003d 0, 1 , 2, 3 etc.). In other words, 2, 6, 10, 14 electrons, etc. can be stored in aromatic fields. The same rule applies only to monocyclic spoluks.
Molecules, like a combination of characteristic structural, energy and chemical powers, entangled with a flat cyclic structure with a system of connections, established by delocalization.p-electrons are called aromatic floors.
The only characteristics that allow you to superbly classify as aromatic or non-aromatic, not essential. The main characteristics of aromatic spoluks are:
skhilnіst to reactions of substitution, but not to come (simply easier, historically the first sign, butt - benzene, on vіdmіnu vіd ethylene not znebarvlyuє bromine water)
· Vigrash in energy, in pairs with a system of non-conjugated connecting links. It is also called Energy Resonance (the improved method is Energy Resonance Dewar) (the great flooring is great, that the molecule knows a significant transformation to reach the aromatic state, for example, cyclohexadiene is easily dehydrogenated to benzene, two and triatomic phenols are important in form).
· Manifestation of ring magnetic struma;
· The presence of the plane itself (minimally created), in which lie all (or not all - homoaromaticity) atoms that make up the aromatic system. At the same ring of p-electrons, which are established at the same time under the linkages (or electrons, which enter into the ring of heteroatoms), lie above and below the plane of the aromatic system.
· Practically zavzhdim dotremuetsya Hückel's Rule: an aromatic system is less likely to avenge (at kіltsi) 4n + 2 electrons (de n = 0, 1, 2, ...). A system that avenges 4n electrons is antiaromatic (in a simpler sense, it means too much energy in the molecule, unevenness of the bonds, low stability - scalability to reactions).
(chlorobenzene) + H2O


Pokhіdnih benzene Z 6 N 5 X under the infusion of the intercessor X the equanimity of the distribution of the l-electronic gloom is broken, tobto. є areas of promotion and reduced electronic power. That is why the lightness of the electro-attack lies directly in the nature of the intercessor.
Defenders in the benzene ring can take substitution reactions ( active advocates), and so improve the speed of the reaction ( deactivating intercessors).