How to revise tasks from modules. Rivnyannya іz module. Basic concepts and power
The term (module) in the literal translation from Latin means "zahіd". The concept was introduced into mathematics by the English scientist R. Kotes. And the German mathematician K. Wejerstrass, having learned about the sign of the module, is a symbol, which means that the hour of writing is meant to be understood.
In contact with
First of all, you understand in mathematics for the program of the 6th grade of the middle school. Zgіdno with one іz vyznachen, modulo - tse absolute value of the number. In other words, in order to recognize the modulus of a decimal number, it is necessary to select its sign.
Graphically absolute value but yak |a|.
The main idea of rice is understood by the fact that the wine is a non-negative value.
Numbers, which seem to be one and the same as a sign, are called opposites. If the value is positive, the opposite to it will be negative, and zero will be opposite to itself.
geometric value
In order to understand the concept of the module from the position of the geometry, it is meaningful to see it, it is possible to make it in single rows from the cob of coordinates to the given point. The purpose of the designation is to expand the geometrical sense of the last term.

Graphically, you can say it like this: |a| = O.A.
Power of absolute value
Below will be looked at all the mathematical powers of this understanding and the way to write down the letters of the words:

Features
 When talking about the development of mathematical equalities and inconsistencies, which have a module, it is necessary to remember that their expression is necessary to recognize the sign.
When talking about the development of mathematical equalities and inconsistencies, which have a module, it is necessary to remember that their expression is necessary to recognize the sign.
For example, as a sign of absolute value, to take away a certain mathematical virase, before it, as a module, it is necessary to secure a fictitious mathematical designation.
|A + 5| = A + 5, yakscho, A more or more equals zero.
5-A if A is less than zero.
In some vipadkah, the sign can unambiguously develop for any sign of the change.
Let's look at one more example. Let us consider the coordinate line, denoting all the numerical values of the absolute value of which will be 5.
For the cob, it is necessary to cross the coordinate line, mark the coordinate line on it and set the size of a single wedge. In addition, the mother is directly to blame. Now it is necessary to apply rosettes on this straight line, as to adjust the size of a single winding.
In this order, we can say that there will be two points on the coordinate line that will tick us, with values 5 and -5.
One of the most interesting topics for uchnіv is rozvyazannya rivnyan, scho to avenge the change under the sign of the module. Let's take a look at the cob, why is it tied? Why, for example, are square equals more children clattering like peas, and with such far from the best understanding, like a module, can there be more problems?
In my opinion, all the folds are due to the existence of clearly formulated rules for the implementation of the module. So, virishyuyuchi square equal, learners know exactly what it is necessary for you to write down the formula of the discriminant, and then the formula of the root of the square equal. And what about the robit, how about the module being fixed on equal ground? We will try to clearly describe the necessary plan for the time, if it is equal to avenge the unknown under the sign of the module. We will bring a sprat of applications to the skin drop.
Ale for the cob module designation. Father, modulus of number a called the same number, like a I can't see -a, which is the number a less than zero. You can write it like this:
|a| = a if a ≥ 0 and |a| = -a, same as a< 0
Speaking about the geometrical sense of the module, the next thing to remember is that the skin decimal number has a single point on the numerical axis - її to  coordinate. So the axis, the module or the absolute value of the number, is called the distance from the center of the point to the cob in the numerical axis. Always be given a positive number. In this order, the modulus of any negative number is positive. Before speech, learn at what stage a lot of learners start to stray. The module may have a number, and the result of the module's input is always a positive number.
coordinate. So the axis, the module or the absolute value of the number, is called the distance from the center of the point to the cob in the numerical axis. Always be given a positive number. In this order, the modulus of any negative number is positive. Before speech, learn at what stage a lot of learners start to stray. The module may have a number, and the result of the module's input is always a positive number.
Now let's move on without a hitch to the opening of the river.
1. Perspective equal to mind | \u003d s, de s - deisne number. The price can be checked for the help of the module.
All current numbers are divided into three groups: tі, which is greater than zero, tі, which is less than zero, and the third group is the whole number 0. Let's write down the solution for the visual scheme:
(±c, if s > 0
Yakscho | x | = c, then x = (0, so c = 0
(no root, yakscho z< 0
1) | = 5, because 5> 0, then x = ±5;
2) | = -5 because -five< 0, то уравнение не имеет корней;
3) | = 0 then x = 0.
2. Equal to mind | f(x) | = b de b > 0. To complete this alignment, you need to get the module. Robimo tse: f(x) = b chi f(x) = -b. Now it is necessary to repair the skin from the otrimanih equals. Yakshcho at the weekend Rivnian b< 0, решений не будет.
1) | x + 2 | = 4, because 4 > 0, then
x + 2 = 4 or x + 2 = -4
2) | x 2 - 5 | = 11, because 11 > 0, then
x 2 - 5 = 11 or x 2 - 5 = -11
x 2 = 16 x 2 = -6
x = ± 4 no root
3) | x 2 - 5x | = -8, because -8< 0, то уравнение не имеет корней.
3. Rivnyannya mind | f(x) | = g(x). For the replacement of the module, such a solution is equal to the mother, for example, part of the law is greater than zero, tobto. g(x) ≥ 0. Then we can calculate:
f(x) = g(x) or f(x) = -g(x).
1) | 2x - 1 | \u003d 5x - 10. The cost of matima is the root, yakscho 5x - 10 ≥ 0. The very beginning of the rozvyazannya of such rivnas.
1. O.D.Z. 5x – 10 ≥ 0
2. Solutions:
2x - 1 = 5x - 10 or 2x - 1 = - (5x - 10)
3. Combined O.D.Z. that decision, we take:
Root x = 11/7 is not suitable for O.D.Z., vin is less than 2, and x = 3 is your mind's satisfaction.
Suggestion: x = 3
2) | x - 1 | = 1 - x 2.
1. O.D.Z. 1 – x 2 ≥ 0
(1 – x)(1 + x) ≥ 0
2. Solutions:
x - 1 = 1 - x 2 or x - 1 = - (1 - x 2)
x 2 + x - 2 = 0 x 2 - x = 0
x = -2 or x = 1 x = 0 or x = 1
3. Joint decision and O.D.Z.:
More than a root is suitable x = 1 and x = 0.
Suggestion: x=0, x=1.
4. Equal to mind | f(x) | = | g(x)|. This is equal to two upcoming equals f(x) = g(x) or f(x) = -g(x).
1) | x 2 - 5x + 7 | = | 2x - 5 |. Tse equal equal to two will come:
x 2 - 5x + 7 = 2x - 5 or x 2 - 5x +7 = -2x + 5
x 2 - 7x + 12 = 0 x 2 - 3x + 2 = 0
x = 3 or x = 4 x = 2 or x = 1
Suggestion: x = 1, x = 2, x = 3, x = 4.
5. Rivnyannya, yakі vyrіshuyusya way of substitution (replace change). The Danish solution method is easiest to explain on a specific application. So, let's give a square equal to the module:
x 2 – 6|x| + 5 = 0. For the quality of the module x 2 = |x| 2 , that can be rewritten like this:
|x| 2 - 6 | x | + 5 = 0. Let's change | = t ≥ 0, then math:
t 2 - 6t + 5 \u003d 0. Considering the given equal, we assume that t \u003d 1 or t \u003d 5. Let's turn to replace:
|x| = 1 chi |x| = 5
x = ±1 x = ±5
Suggestion: x=-5, x=-1, x=1, x=5.
Let's look at another example:
x 2 + | – 2 = 0. For module quality x 2 = |x| 2 , to
|x| 2+ |x| - 2 = 0. Let's change | x | = t ≥ 0 then i:
t 2 + t - 2 \u003d 0. Virishingly given equal, it is acceptable, t \u003d -2 or t \u003d 1. Let's turn to replace:
|x| = -2 chi |x| = 1
No root x = ± 1
Suggestion: x=-1, x=1.
6. Another type of alignment is alignment with a "foldable" module. Up to such equalities one can see the equalization, in which there are modules in modules. Rivnyannya tsgogo mind can be violated, blocking the power of the module.
1) |3 – |x|| \u003d 4. D_yatimemo is the same, like in equals of another type. Because 4 > 0, then we take two equalities:
3 - | x | = 4 chi 3 – |x| = -4.
Now virazimo at the skin level module x, todi | = -1 chi |x| = 7.
Virishuemo skin from otrimanih equal. The first equal does not have a root, because -one< 0, а во втором x = ±7.
Verify x=-7, x=7.
2) | 3 + | x + 1 | | = 5
3 + | x + 1 | = 5 chi 3 + |x + 1| = -5
|x + 1| = 2 | x + 1 | = -8
x + 1 = 2 or x + 1 = -2. There is no root.
Suggestion: x=-3, x=1.
Іsnuє shchey and universal method of rozv'yazannya іvnyan іz module. Tse method of intervals. Ale mi yogo looked at.
blog.website, with a new or private copy of the material sent on the original binding.
MBOU ZOSh No. 17 m. Ivanova
« Rivnyannya with the module "
Methodical development
Stocked
teacher of mathematics
Lebedeva N.V.20010
Explanatory note
Section 1. Intro
Section 2. Main Powers Section 3. Geometric interpretation of the concept of the modulus of a number Section 4. Graph of the function y = | Section 5. Mental cognitionPart 2
Razdіl 1.Rivnyannya mind | F(x) | = m (easiest) Section 2. Equal to the form F(|х|) = m Section 3. Equal to the mind | F(x) | = G(x) Section 4. Equal to mind | F(x) | = ± F(x) (beautiful) Section 5. Equal to the mind | F(x) | = | G(x) | Rozdіl 6. Apply the tie of non-standard rivn Section 7. Equal to the mind | F(x) | + | G(x) | = 0 Section 8. Equal to the mind | a 1 x ± 1 | ± |a 2 x ± 2 | ± …|a n x ± y n | = m Section 9Chapter 3
Section 1. Trigonometric alignment Partition 2. Showing the alignment Section 3. Logarithmic Equation Section 4. Irrational alignment Section 5. Order for the promotion of folding Vidpovidі to the right List of referencesExplanatory note.
The concept of the absolute value (modulus) of a decimal number is one of the essences of its characteristics. Tse understanding may have become very wide in various branches of the physical, mathematical and technical sciences. In practice, for the course of mathematics in secondary school, up to the Program of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, the understanding of the “absolute value of a number” is noted repeatedly: in the 6th grade, the designation of the module is introduced, its geometrical zmist; in the 8th class, the understanding of the absolute error is formed; in the 11th class, the understanding is heard in the division “Korin nth step." Dosvіd vykladannya pokaєє, shcho uchnі often stikayutsya z difficulties pіd hіvіshennya zavdan, scho vmagayut knowledge of the given material, and often miss, without proceeding to vikonannya. The texts of examination tasks for the course of the 9th and 11th grades also include similar tasks. In addition, moreover, if you present to the graduates of the schools of the VNZ, they are rehabilitated, and, for the most part, even less than the school program. For life in the future, it is even more important to mold the mathematical style of thought, which manifests itself in the singing of Rozum's newcomers. In the process of executing the task of the modules, it is necessary to zastosovuvat such a decision, as a further specification, analysis, classification and systematization, analogy. The versatility of similar tasks allows you to reconsider the knowledge of the main divisions of the school course, the riven of logical thought, and the beginnings of the basic activity. Tsya robot is assigned to one of the divisions - the virishennya rivnyan, scho to avenge the module. The won is made up of three divisions. In the first division, the main concepts and the most important theoretical concepts are introduced. At the other, nine main types of equalizations are shown, to avenge the module, methods of their perfection are looked at, butts of different equalities of folding are picked up. The third one has folding and non-standard alignment (trigonometric, display, logarithmic and irrational). Up to the dermal type, it is right for an independent variant (various indications and instructions are given). The main purpose of this work is to provide methodical assistance to students in preparation for lessons and in the organization of optional courses. The material can also be used as a heading guide for high school students. The manager, encouraged in work, cica and don’t start simple at the top, which allows you to increase the initial motivation of the students more aware, change your health, improve the training of graduate students to the entrance to the VNZ. Differentiation of the right to proponate the right to transfer the transition from the reproductive level to the material to the creative one, and to inspire the ability to learn to develop one’s knowledge of the hour of accomplishment of non-standard tasks.Section 1. Intro.
Section 1. Appointment of the absolute value .
Appointment : The absolute value (modulus) of a decimal number but called an unknown number: but or -BUT. Designation: │ but │ The entry reads like this: “the modulus of the number a” or “the absolute value of the number a”│ and if a > 0
│a│ = │ 0, so a = 0 (1)
│ - a, like aApply: 1) │2,5│ = 2,5 2) │-7│ = 7 3) │1 - √2│ = √2 – 1
- Expand Virazu module:
Section 2. Main characteristics.
Let's take a look at the main power of absolute magnitude. Power #1: Protilezhnі number mayut equal modules, tobto. │а│=│-а│ Let's show the fidelity of jealousy. Let's write down the number - but : │- a│= (2) Equal marriages (1) and (2). It is obvious that the designation of the absolute values of numbers butі - but run away. Otzhe, │а│=│-а│When looking at the advancing authorities, we mix in their formulas, so that their proof can be found in Power #2: The absolute value of the sum of the final number of actual numbers does not exceed the sum of the absolute values of the additional numbers: Power #3: The absolute value of the difference between two real numbers does not exceed the sum of their absolute values: │а - в│ ≤│а│+│в│ Power #4: The absolute value of the creation of the end number of the real numbers is more important for the completion of the absolute values of the multipliers: Power #5: The absolute value of the part of the real numbers is equal to the private one of their absolute values:

Section 3. Geometrical interpretation of the concept of the modulus of a number.
You can put a point on the numerical straight line for the skin number, as if it were a geometric representation of the number. The skin dot on the numerical straight line shows you to the cob for the sake of it. dozhina vіdіzka vіd vіdlіku vіdlіku to tsієї point. Tsya vіdstan priymaєtsya zavzhd as a non-negative value. To this end, the dozhina of a double wedge will be a geometric interpretation of the absolute value of the current number.
A geometric illustration was given, confirming the accuracy of No. 1, tobto. modules of opposite numbers are equal. It is easy to understand the justice of equality: │x - a│= │a - x│. It is also more obvious that the solution is equal │х│= m, de m ≥ 0, and x 1.2 itself = ± m. Apply: 1) │х│= 4 x 1.2 = ± 4 2) │х - 3│= 1
 x 1.2 = 2; 4
x 1.2 = 2; 4 Section 4. Graph of the function y = │х│
The scope of the function is all actual numbers.Rozdіl 5. Smart cognition.
Nadal, when looking at the butts of the rose, the rivnyan will be vikoristan such a clever designation: ( - sign of system [ - sign of marriage When the system of equalities (irregularities) is rozvyazanny, there is a gap between the solutions to enter the system of equalities (irregularities). When the marriage of rivnyan (irregularities) is broken, there is a general decision that enters to the marriage of rivnyan (irregularities).Chapter 2
For whom we have divided, we can look at ways of developing algebra equal, which can be done with one or more module.Section 1. Equal to the mind │F(х)│= m
Rivnyanna tsgogo mind is called the simplest. There may be a solution even and only if m ≥ 0. For the purpose of the module, the difference is equal to the combination of two equals: │ F(x)│=m
 Apply:
Apply:
№1. Untie equalization: │7х - 2│= 9


 Suggestion: x 1
= - 1; X 2
= 1
4
/
7
№2
Suggestion: x 1
= - 1; X 2
= 1
4
/
7
№2
│x 2 + 3x + 1│= 1

 x 2 + 3x + 2 = 0 x 2 + 3x = 0 x 1 = -1; x 2 \u003d -2 x (x + 3) \u003d 0 x 1 \u003d 0; x 2 = -3 Vidpovid: the sum of the roots is dorіvnyu - 2.№3
x 2 + 3x + 2 = 0 x 2 + 3x = 0 x 1 = -1; x 2 \u003d -2 x (x + 3) \u003d 0 x 1 \u003d 0; x 2 = -3 Vidpovid: the sum of the roots is dorіvnyu - 2.№3
│x 4 -5x 2 + 2│= 2 x 4 - 5x 2 = 0 x 4 - 5x 2 + 4 = 0 x 2 (x 2 - 5) = 0 significant x 2 = m, m ≥ 0 x = 0 ; ±√5 m 2 – 5m + 4 = 0 m = 1; 4 - offensive values satisfy the mind m ≥ 0 x 2 = 1 x 2 = 4 x = ± 1 x = ± 2 Verdict: number of roots of rivers 7. Right:
№1. Razv'yazhit rivnyannya and show the sum of roots: │х - 5 │ = 3 №2 . Expand the equation and show the smaller root: │х 2 + х│ = 0 №3 . Razv'yazhit rivnyannya and show the greater root: │x 2 - 5x + 4 │ \u003d 4 №4 .Rіshіt rіvnyannya i vkazhіt qіliy korіn: │2х 2 – 7х + 6│= 1 №5 .Rіshіt rіvnyannya i vkazhіt kіlkіst korіnіv: │х 4 – 13х 2 + 50│= 14
Section 2. Equal to the mind F(│х│) = m
The argument of the function in the left part is changed under the sign of the module, and the rights of the part are in the change. Let's take a look at two ways of rozv'yazannya rіvnyan this kind. 1 way: According to the absolute value, the difference is equal to the combination of the two systems. In the skin of these, the mind submodular viraz is superimposed. F(│х│) =m Since the function F(│х│) is paired for the entire range of assignment, then the root equals F(х) = m і F(-х) = m are pairs of opposite numbers. Therefore, to complete one of the systems (when looking at the applications in the indicated way, one system will be solved). 2 way: Zastosuvannya method of zaprovadzhennya new zminnoy. With this, the value │х│= a de a ≥ 0 is introduced.
Since the function F(│х│) is paired for the entire range of assignment, then the root equals F(х) = m і F(-х) = m are pairs of opposite numbers. Therefore, to complete one of the systems (when looking at the applications in the indicated way, one system will be solved). 2 way: Zastosuvannya method of zaprovadzhennya new zminnoy. With this, the value │х│= a de a ≥ 0 is introduced. Apply: №1 . Razv'yazhit rivnyannya: 3x 2 - 4│х│= - 1 We'll speed up the introduction of a new change. Significantly │х│= a, de a ≥ 0. Removal of alignment 3a 2 - 4a + 1 \u003d 0 D \u003d 16 - 12 \u003d 4 a 1 \u003d 1 a 2 \u003d 1/3 │х│= 1/3. The skin has two roots. Suggestion: x 1 = 1; X 2 = - 1; X 3 = 1 / 3 ; X 4 = - 1 / 3 . №2. Untie equal: 5x 2 + 3│x│- 1 \u003d 1 / 2 │x│ + 3x 2
 We know the solution to the first marriage system: 4x 2 + 5x - 2 \u003d 0 D \u003d 57 x 1 \u003d -5 + √57 / 8 x 2 \u003d -5-√57 / 8 Dearly, that x 2 does not satisfy the mind x ≥ 0. Solutions another system will be a number that is proportional to x 1 . Suggestion: x 1
=
-5+√57
/
8
; X 2
=
5-√57
/
8
.№3
.
Rise equal: х 4 – │х│= 0 Significantly │х│= a, de a ≥ 0. Take equal a 4 – a = 0 a (a 3 – 1) = 0 a 1 = 0 a 2 = 1 Turn to the reverse change: │х│=0 and │х│= 1 x = 0; ± 1 Suggestion: x 1
= 0; X 2
= 1; X 3
= - 1.
We know the solution to the first marriage system: 4x 2 + 5x - 2 \u003d 0 D \u003d 57 x 1 \u003d -5 + √57 / 8 x 2 \u003d -5-√57 / 8 Dearly, that x 2 does not satisfy the mind x ≥ 0. Solutions another system will be a number that is proportional to x 1 . Suggestion: x 1
=
-5+√57
/
8
; X 2
=
5-√57
/
8
.№3
.
Rise equal: х 4 – │х│= 0 Significantly │х│= a, de a ≥ 0. Take equal a 4 – a = 0 a (a 3 – 1) = 0 a 1 = 0 a 2 = 1 Turn to the reverse change: │х│=0 and │х│= 1 x = 0; ± 1 Suggestion: x 1
= 0; X 2
= 1; X 3
= - 1.
Right: №6. Razv'yazhit rivnyannya: 2│х│ - 4.5 = 5 - 3/8 │х│ №7 . Razv'yazhit rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі indicate the number of roots: 3х 2 - 7│х│ + 2 = 0 №8 . Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt qіlі solution: х 4 + │х│ - 2 = 0
Section 3. Equal to the mind │F(х)│ = G(х)
The rights of a part of a given species to lie in change and, therefore, it can be solved even and less so, if the rights of a part of the function G (x) ≥ 0. A part of the equal can be found in two ways: 1 way: Standard, based on the development of the module, vyhodyachi z yogo appointment and polagaє in an equal transition to the combination of two systems. │ F(x)│ =G(X)
 Denmark is able to rationally twist at times folding for the function G (x) and less folding - for the function F (x), so the variance of irregularities is transferred to the function F (x). 2 way: Perebuvayut at the transition to an equally strong system, at the same time the right part of the mind is superimposed. │ F(x)│=
G(x)
Denmark is able to rationally twist at times folding for the function G (x) and less folding - for the function F (x), so the variance of irregularities is transferred to the function F (x). 2 way: Perebuvayut at the transition to an equally strong system, at the same time the right part of the mind is superimposed. │ F(x)│=
G(x)

 The Danish way of stowing is more efficient, which means that for the function G(x) there is less folding, lower for the function F(x), so that the breakdown of unevenness G(x) ≥ 0 is transferred. option. Apply:
№1.
Untie equalization: │x + 2│= 6 -2x
The Danish way of stowing is more efficient, which means that for the function G(x) there is less folding, lower for the function F(x), so that the breakdown of unevenness G(x) ≥ 0 is transferred. option. Apply:
№1.
Untie equalization: │x + 2│= 6 -2x  (1 way) Verify: x = 1 1
/
3
№2.
(1 way) Verify: x = 1 1
/
3
№2.
│x 2 - 2x - 1 │ \u003d 2 (x + 1)
 (2 way) Verdict: Tver root - 3.
(2 way) Verdict: Tver root - 3.№3. Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots:
│x - 6 │ \u003d x 2 - 5x + 9

Verdict: the sum of the roots is good 4.
Right: №9. │x + 4│= - 3x №10. Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі specify the number of rozv'yazkіv: │х 2 + х - 1│= 2х - 1 №11 . Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt dobutok root: │x + 3│= x 2 + x - 6
Section 4. Equal to the mind │F(x)│= F(x) and │F(x)│= - F(x)
Rivnyannya tsgogo mind is sometimes called "beautiful". Shards of the right of a part of the equal to lie in the form of a change, the decision is to be made and the same, if the right of the part is non-negative. Therefore, vihіdnі іvnіnіnі іvnіnіnі іvnosіlnі nerіvnosti:│F(x)│= F(x) F(x) ≥ 0 and │F(x)│= - F(x) F(x) Apply: №1 . Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show a lesser qіliy root: │5x - 3│= 5x - 3 5x - 3 ≥ 0 5x ≥ 3 x ≥ 0.6 Verify: x = 1№2. Razvyazіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vіdvіdі vkazhіt dovzhіnі promіzh: │х 2 - 9 │= 9 - х 2 х 2 - 9 ≤ 0 (х - 3) (х + 3) ≤ 0 [- 3; 3] Vidpovid: dozhina promizhku dorіvnyuє 6.№3 . Splitting is equal, at the same time, enter the number of multiple splits: │2 + x - x 2 │ = 2 + x - x 2 2 + x - x 2 ≥ 0 x 2 - x - 2 ≤ 0 [- 1; 2] Suggestion: 4 whole solutions.№4 . Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt the greatest root:
│4 - x -
 │= 4 – x –
│= 4 – x –  x 2 - 5x + 5 \u003d 0 D \u003d 5 x 1.2 \u003d
x 2 - 5x + 5 \u003d 0 D \u003d 5 x 1.2 \u003d  ≈ 1,4
≈ 1,4Verdict: x = 3.
Right:
№12.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt qіliy korіn: │х 2 + 6х + 8 │ = x 2 + 6х + 8 №13.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, y vіdpovіdі specify the number of tіlih solutions: │13x – x 2 - 36│+ x 2 – 13x + 36 = 0 №14.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, in vіdpovіdі indicate the whole number, which is not the root of іvnyannia: 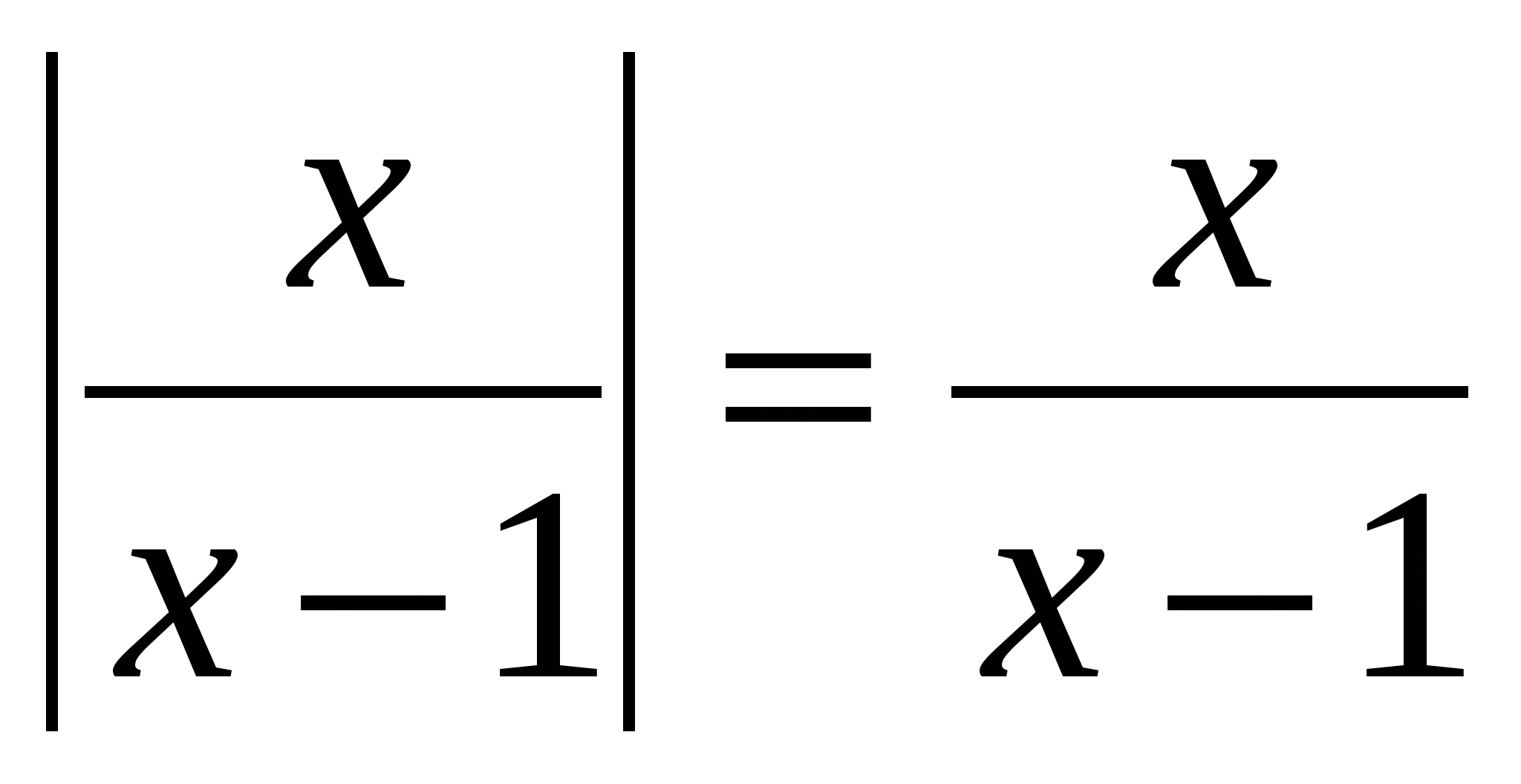
Section 5. Equal to the mind │F(x)│= │G(x)│
Shards of insulting parts of equal are non-negative, then the solution conveys a view of two vipadkiv: pіdmodulnі virazi vіvnі chi protilezhnі behind the sign. Otzhe, vyhіdne rіvnyannja іvnostrіvnі sukupnі tvoh іvnyan: │ F(x)│= │ G(x)│ Apply:
№1.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt qіliy korіn: │х + 3│=│2х - 1│
Apply:
№1.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt qіliy korіn: │х + 3│=│2х - 1│ 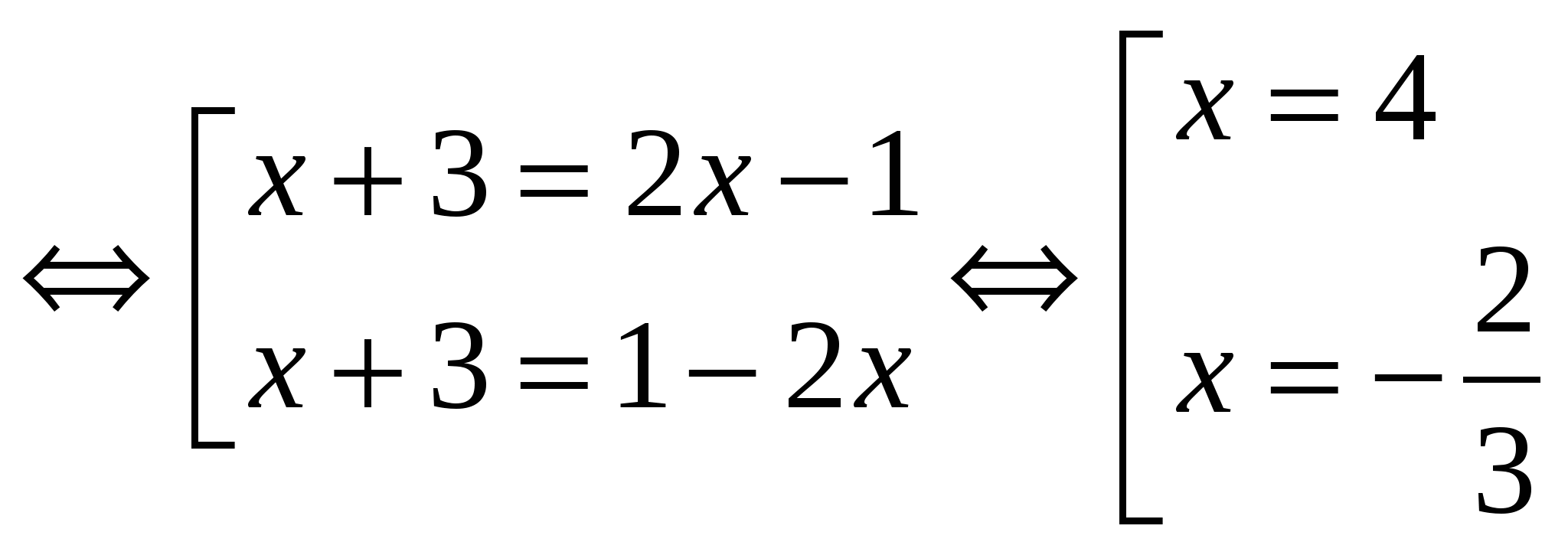 Suggestion: whole root x = 4.№2.
Untie the river: │
x - x 2 - 1│ \u003d │2x - 3 - x 2 │
Suggestion: whole root x = 4.№2.
Untie the river: │
x - x 2 - 1│ \u003d │2x - 3 - x 2 │  Verdict: x = 2.№3
.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, in vіdpovіdі vkazhіt dobutok root:
Verdict: x = 2.№3
.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, in vіdpovіdі vkazhіt dobutok root: 


 Roots equal 4x2 + 2x - 1 = 0x1.2 = - 1±√5 / 4 Vidpovid: dobutok korіnnya dorіvnyuє - 0.25. Right:
№15
. Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt tsіle solution: │х 2 – 3х + 2│= │х 2 + 6х - 1│ №16.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt less root: │5x - 3│=│7 - x│ №17
. Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots:
Roots equal 4x2 + 2x - 1 = 0x1.2 = - 1±√5 / 4 Vidpovid: dobutok korіnnya dorіvnyuє - 0.25. Right:
№15
. Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt tsіle solution: │х 2 – 3х + 2│= │х 2 + 6х - 1│ №16.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt less root: │5x - 3│=│7 - x│ №17
. Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: 
Rozdіl 6. Apply the tie of non-standard rivn
We can look at examples of non-standard rivnyans, for example, the absolute value of which depends on the appointments. Apply:№1.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt sum of roots: х │х│- 5х – 6 = 0  Suggestion: the sum of the roots is 1 №2.
.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt lesser root: х 2 - 4х ·
Suggestion: the sum of the roots is 1 №2.
.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt lesser root: х 2 - 4х · 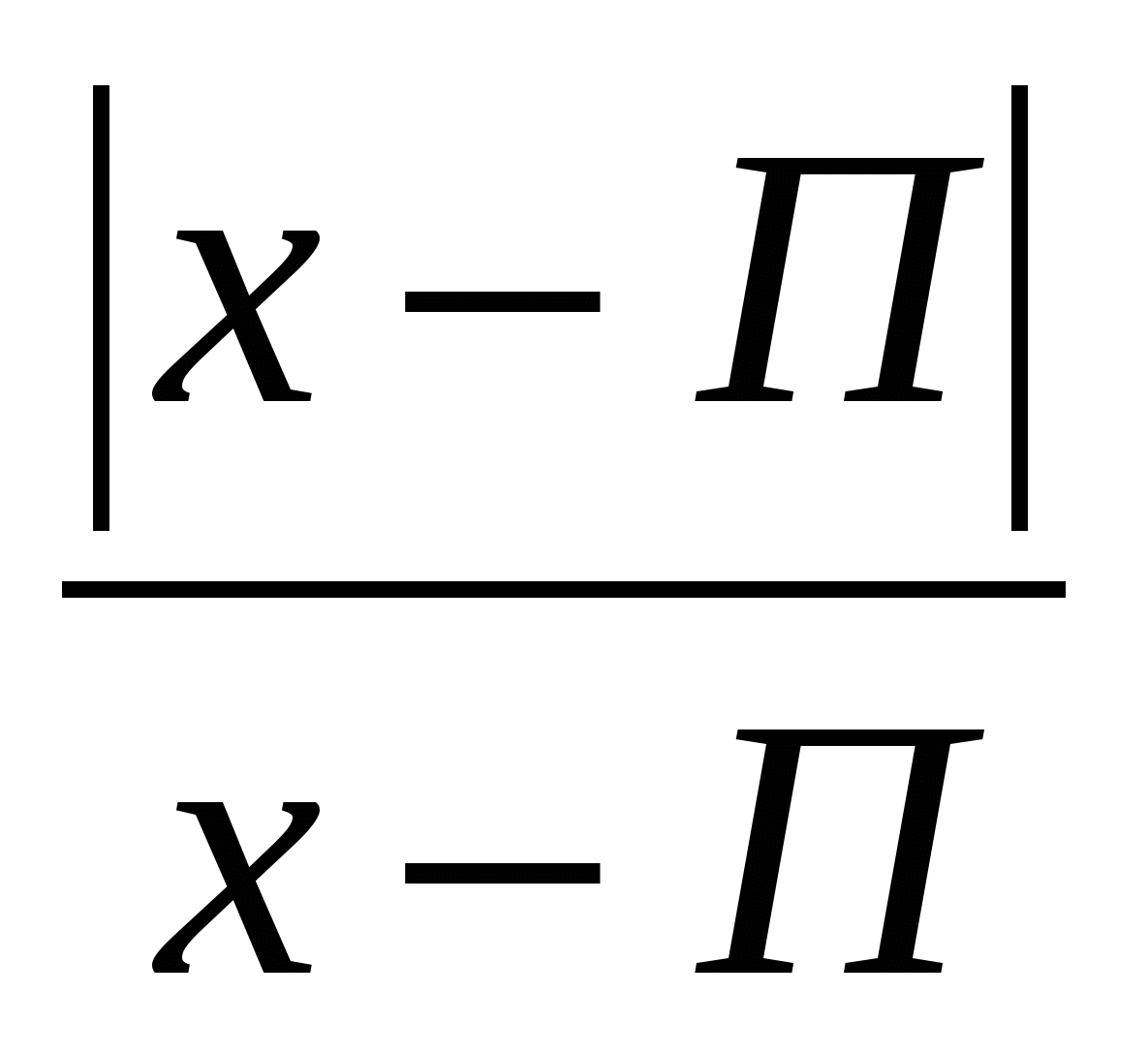 - 5 = 0
- 5 = 0 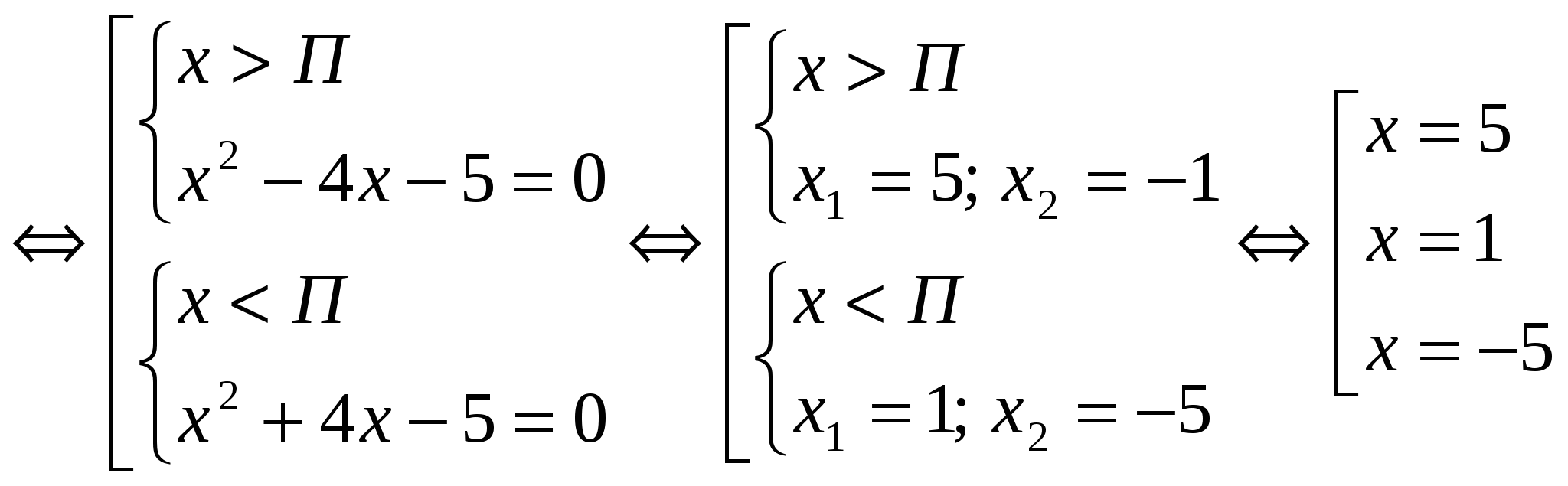 Suggestion: smaller root x = - 5. №3.
Untie the river:
Suggestion: smaller root x = - 5. №3.
Untie the river:  Verify: x = -1. Right:
№18.
Razv'yazhіt equal and show the sum of the roots: x │3x + 5│= 3x 2 + 4x + 3
Verify: x = -1. Right:
№18.
Razv'yazhіt equal and show the sum of the roots: x │3x + 5│= 3x 2 + 4x + 3
№19.
Untie equal: x 2 - 3x \u003d 
№20.
Untie the river: 
Section 7. Equal to the mind │F(x)│+│G(x)│=0
It is not important to remember that the left part is equal to the sum of non-negative values. Otzhe, in the future, even if it is possible, then even more, if the offense of the dodanki is equal to zero at once. Rivnyannya equally strong systems equal: │ F(x)│+│ G(x)│=0 Apply:
№1
. Untie the river:
Apply:
№1
. Untie the river:  Verdict: x = 2. №2.
Untie the river: Verify: x = 1. Right:
№21.
Untie the river: №22
. Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: №23
. Razv'yazhit rіvnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt kіlkіst іdіnі:
Verdict: x = 2. №2.
Untie the river: Verify: x = 1. Right:
№21.
Untie the river: №22
. Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: №23
. Razv'yazhit rіvnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt kіlkіst іdіnі: Section 8. Equal to the mind │а 1 x + y 1 │±│а 2 x + y 2 │± … │а n x + в n │= m
In order to improve the equality of this mind, the method of intervals is used. If you want to check the last of the modules, then take it n collections of systems, which are too cumbersome and unhandy. Let's look at the method of the interval algorithm: 1). Know the meaning of the change X, For any skins, the module is equal to zero (zero pіdmodulnyh vrazіv): 2). Found values in the number line, as divided into intervals (the number of intervals is probably more n+1
) 3). Significantly, with a certain sign, the skin module is opened to the skin module with a minimum of intervals (when the solution is drawn up, you can choose a numerical straight line, assigning signs to it) 4). Vihіdne rіvnyannya іvnostrіvno sukupnostі n+1
systems, in the skin, among them, the belonging of the change X one of the intervals. Apply:
№1
. Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt the greatest root:
2). Found values in the number line, as divided into intervals (the number of intervals is probably more n+1
) 3). Significantly, with a certain sign, the skin module is opened to the skin module with a minimum of intervals (when the solution is drawn up, you can choose a numerical straight line, assigning signs to it) 4). Vihіdne rіvnyannya іvnostrіvno sukupnostі n+1
systems, in the skin, among them, the belonging of the change X one of the intervals. Apply:
№1
. Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt the greatest root:  one). We know zero submodular viruses: x = 2; x = -3 2). Significantly known values on the number line and significant, with some sign, the skin modulus curves on subintervals:
one). We know zero submodular viruses: x = 2; x = -3 2). Significantly known values on the number line and significant, with some sign, the skin modulus curves on subintervals: x – 2 x – 2 x – 2 - - + - 3 2 x 2x + 6 2x + 6 2x + 6 - + + 3)
 - there is no solution Rivnyannya may have two roots. Vidpovid: maximum root x = 2. №2.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt qіliy korіn:
- there is no solution Rivnyannya may have two roots. Vidpovid: maximum root x = 2. №2.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt qіliy korіn:  one). We know zero submodular viruses: x = 1.5; x = - 1 2). Significantly known value on the number line i is significant, with a certain sign the skin modulus curves on subintervals: x + 1 x + 1 x + 1 - + +
one). We know zero submodular viruses: x = 1.5; x = - 1 2). Significantly known value on the number line i is significant, with a certain sign the skin modulus curves on subintervals: x + 1 x + 1 x + 1 - + + -1 1.5 x 2x - 3 2x - 3 2x - 3 - - +
3).
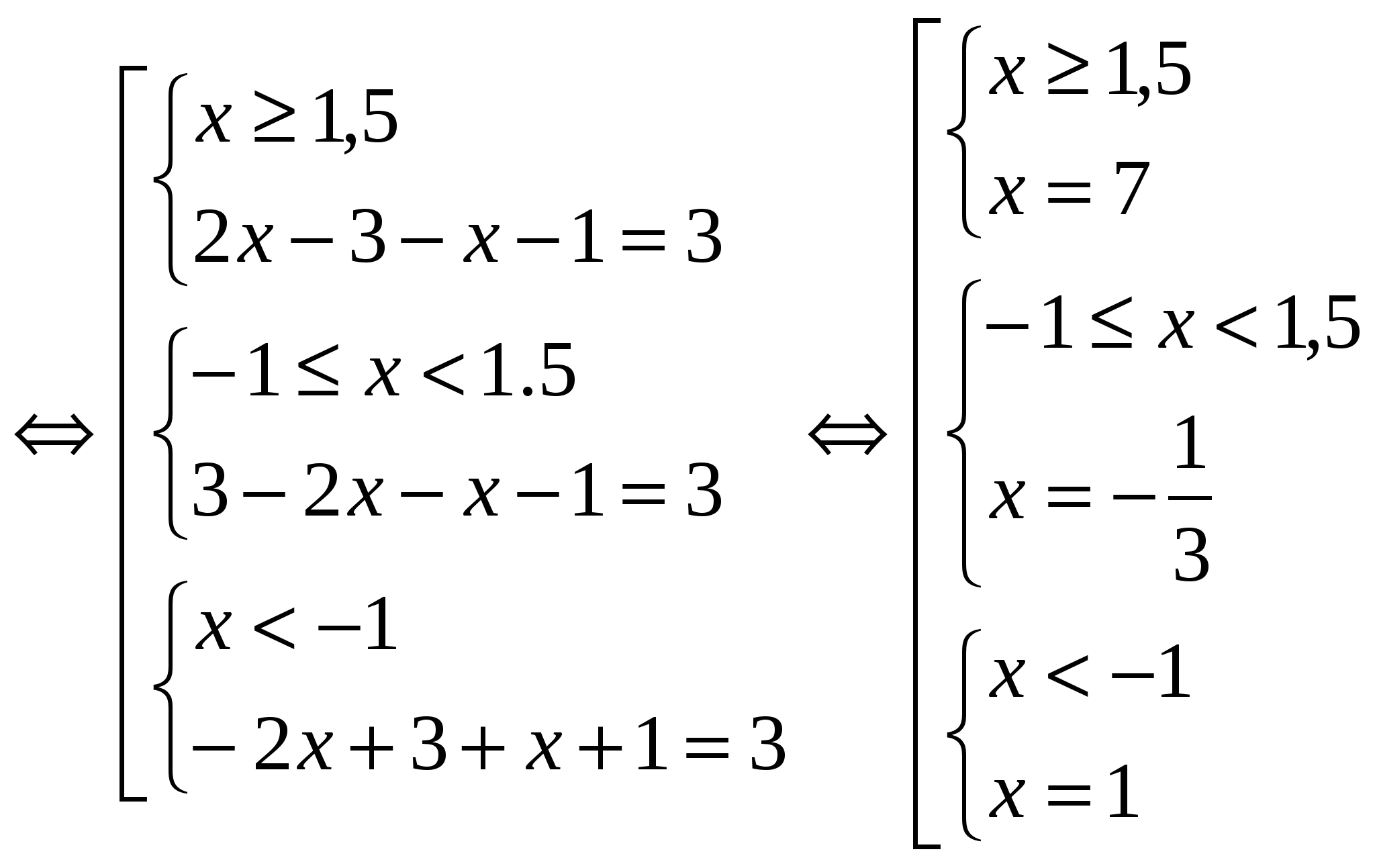 The rest of the system does not have a solution, then, equal can have two roots. At the beginning of the rozv'yazannya ryvnyannya next turn respect for the "-" sign in front of another module. Suggestion: the whole root x = 7. №3.
Razv'yazhit rivnyannya, in vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: 1). We know zero submodular viruses: х = 5; x = 1; x = - 2 2). Significantly known values on the number line and significant, with a certain sign, the skin modulus curves on sub-intervals: х – 5 х – 5 х – 5 х – 5 - - - +
The rest of the system does not have a solution, then, equal can have two roots. At the beginning of the rozv'yazannya ryvnyannya next turn respect for the "-" sign in front of another module. Suggestion: the whole root x = 7. №3.
Razv'yazhit rivnyannya, in vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: 1). We know zero submodular viruses: х = 5; x = 1; x = - 2 2). Significantly known values on the number line and significant, with a certain sign, the skin modulus curves on sub-intervals: х – 5 х – 5 х – 5 х – 5 - - - + -2 1 5 x x – 1 x – 1 x – 1 x – 1 - - + + x + 2 x + 2 x + 2 x + 2 - + + +
3).
 Equation has two roots x = 0 and 2. Verdict: the sum of the roots is 2. №4
.
Razv'yazhit rivnyannya: 1). We know zero submodular viruses: х = 1; x = 2; x = 3. 2). Significantly, with a certain sign, the skin module is taken away from the intervals. 3).
Equation has two roots x = 0 and 2. Verdict: the sum of the roots is 2. №4
.
Razv'yazhit rivnyannya: 1). We know zero submodular viruses: х = 1; x = 2; x = 3. 2). Significantly, with a certain sign, the skin module is taken away from the intervals. 3).  Combined solutions for the first three systems. Suggestion: ; x = 5.
Combined solutions for the first three systems. Suggestion: ; x = 5.Right: №24. Untie the river:
 №25.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: №26.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt lesser root: №27.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt greater root:
№25.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: №26.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt lesser root: №27.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, vіdpovіdі vkazhіt greater root: Section 9
Rivnyannya, scho to avenge a sprinkling of modules, conveys the presence of absolute values in submodular virases. The main principle of the expansion of this type is the following expansion of modules, starting from the old one. At the result, the decision will be made, and the divisions No. 1, No. 3 will be looked at.Apply:
№1.
Untie the river:  Vidpovid: х = 1; - eleven. №2.
Untie the river:
Vidpovid: х = 1; - eleven. №2.
Untie the river:
Vіdpodіd: х = 0; 4; - 4. №3.
Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, in vіdpovіdі vkazhіt dobutok root:  Vidpovid: dobutok root dorivnyu - 8. №4.
Untie the river:
Vidpovid: dobutok root dorivnyu - 8. №4.
Untie the river: 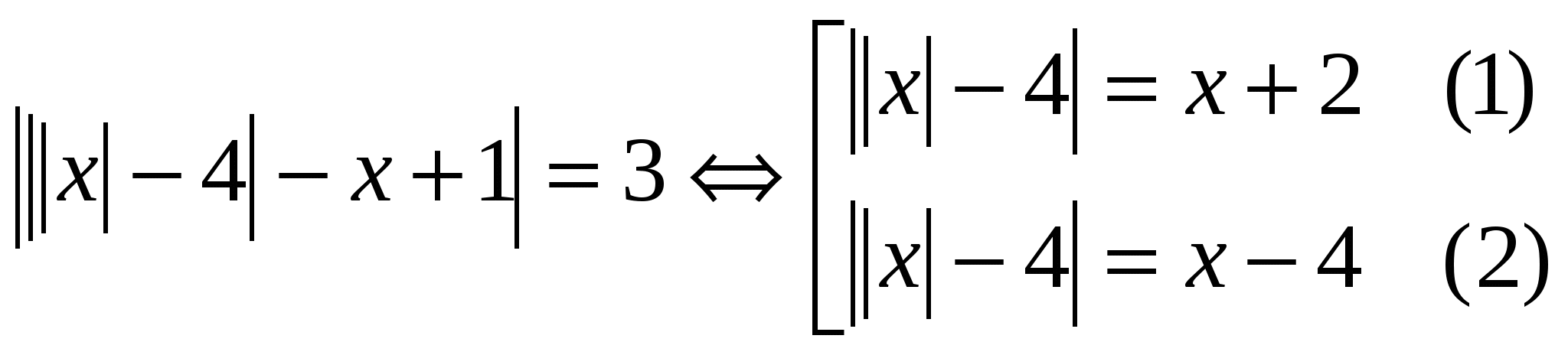 Significantly equal marriage (1)
і (2)
that perceptible solution of the skin of them is okremo for clarity of design. So, as an insult, equal to take more than one module, it is better to make a more equal transition to the totality of systems. (1)
Significantly equal marriage (1)
і (2)
that perceptible solution of the skin of them is okremo for clarity of design. So, as an insult, equal to take more than one module, it is better to make a more equal transition to the totality of systems. (1)
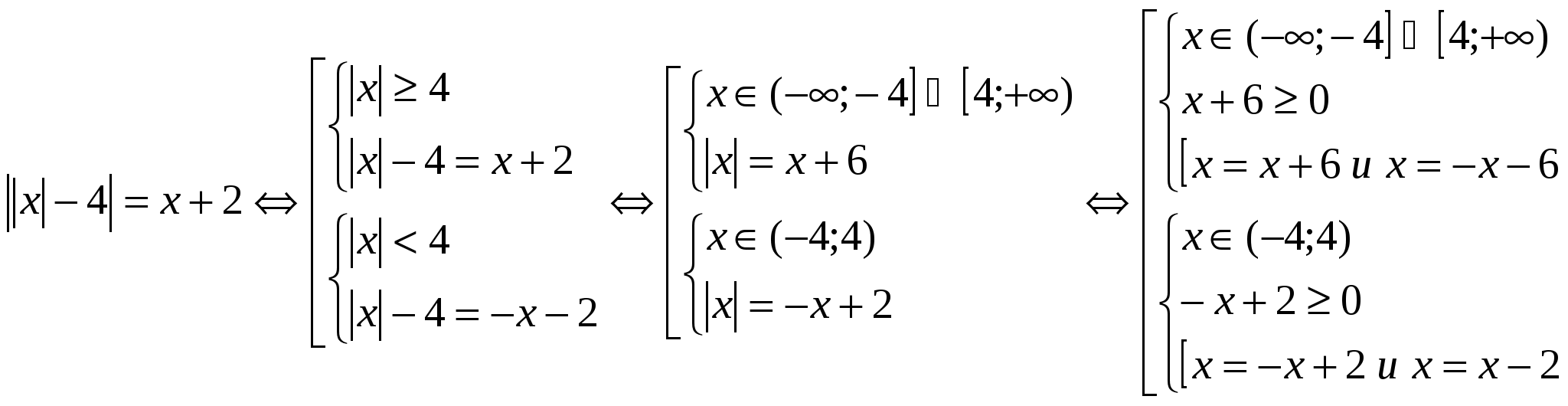
 (2)
(2)
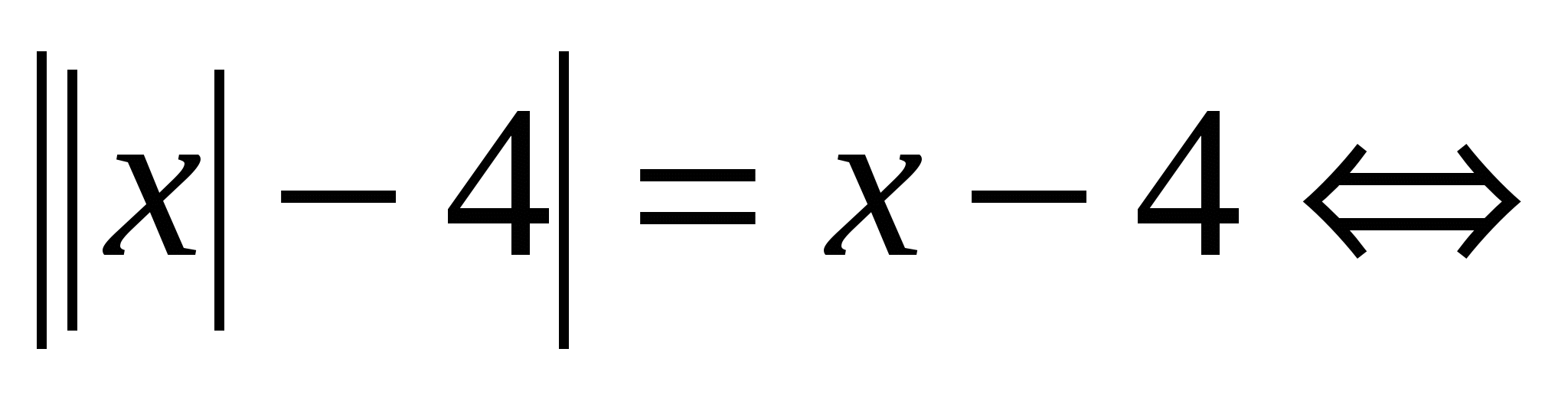
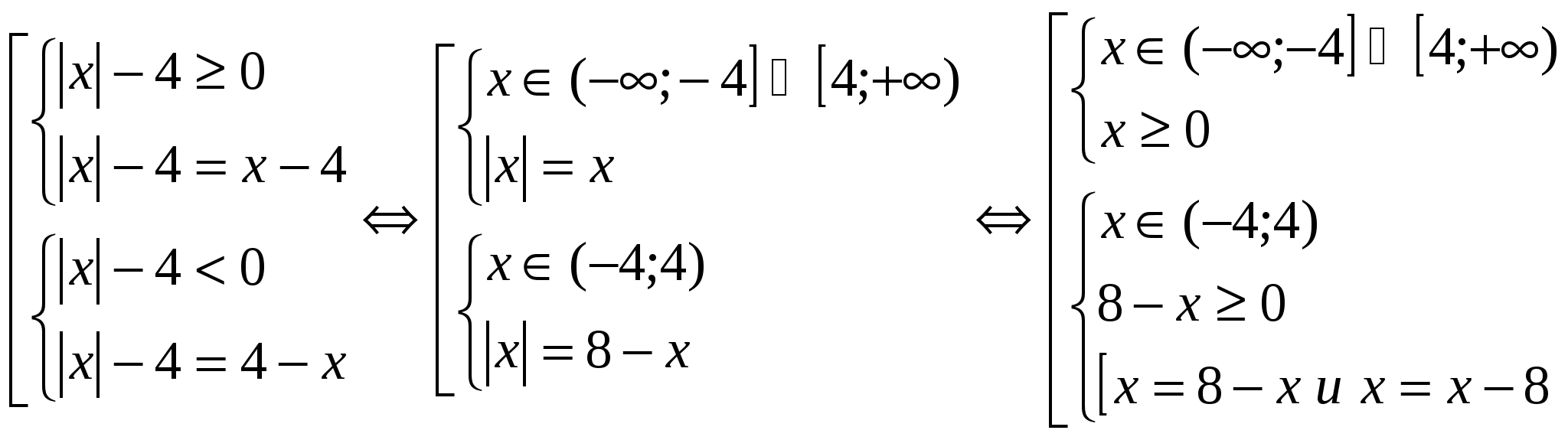
 Suggestion:
Suggestion:
Right:
№36.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt sum of roots: 5 │3x-5│ = 25 x №37.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, as the root is greater than one, at the same time, indicate the sum of the roots: │x + 2│ x - 3x - 10 \u003d 1 №38.
Razvyazіt rivnyannya: 3 │2х -4│ = 9 │х│ №39.
Razv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі vkazhіt number of roots on: 2 │ sin x │ \u003d √2 №40
. Rozv'yazhіt rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі indicate the number of roots:
Section 3. Logarithmic equalization.
Before unleashing the offensive equals, it is necessary to repeat the power of logarithms and logarithmic functions. Apply: №1. Expanding the rіvnyannya, vіdpovіdі vіdvіdі vіdkіt dobutok korіnnya: log 2 (х+1) 2 + log 2 │x+1│ = 6 O.D.Z. x+1≠0 x≠ - 11 fallow: if x ≥ - 1, then log 2 (x+1) 2 + log 2 (x+1) = 6 log 2 (x+1) 3 = log 2 2 6 (x+1) 3 = 2 6 x+1 = 4 x = 3 – brain-pleasing x ≥ - 1 2 upside down: yes x log 2 (x+1) 2 + log 2 (-x-1) = 6 log 2 (x+1) 2 + log 2 (-(x+1)) = 6 log 2 (-(x+1) 3) = log 2 2 6- (x+1) 3 = 2 6- (x+1) = 4 x = - 5 – satisfied mental x - 1
Vidpovid: dobutok root dorivnyu - 15.
№2.
Razv'yazhit rivnyannya, at vіdpovіdі show the sum of roots: lg 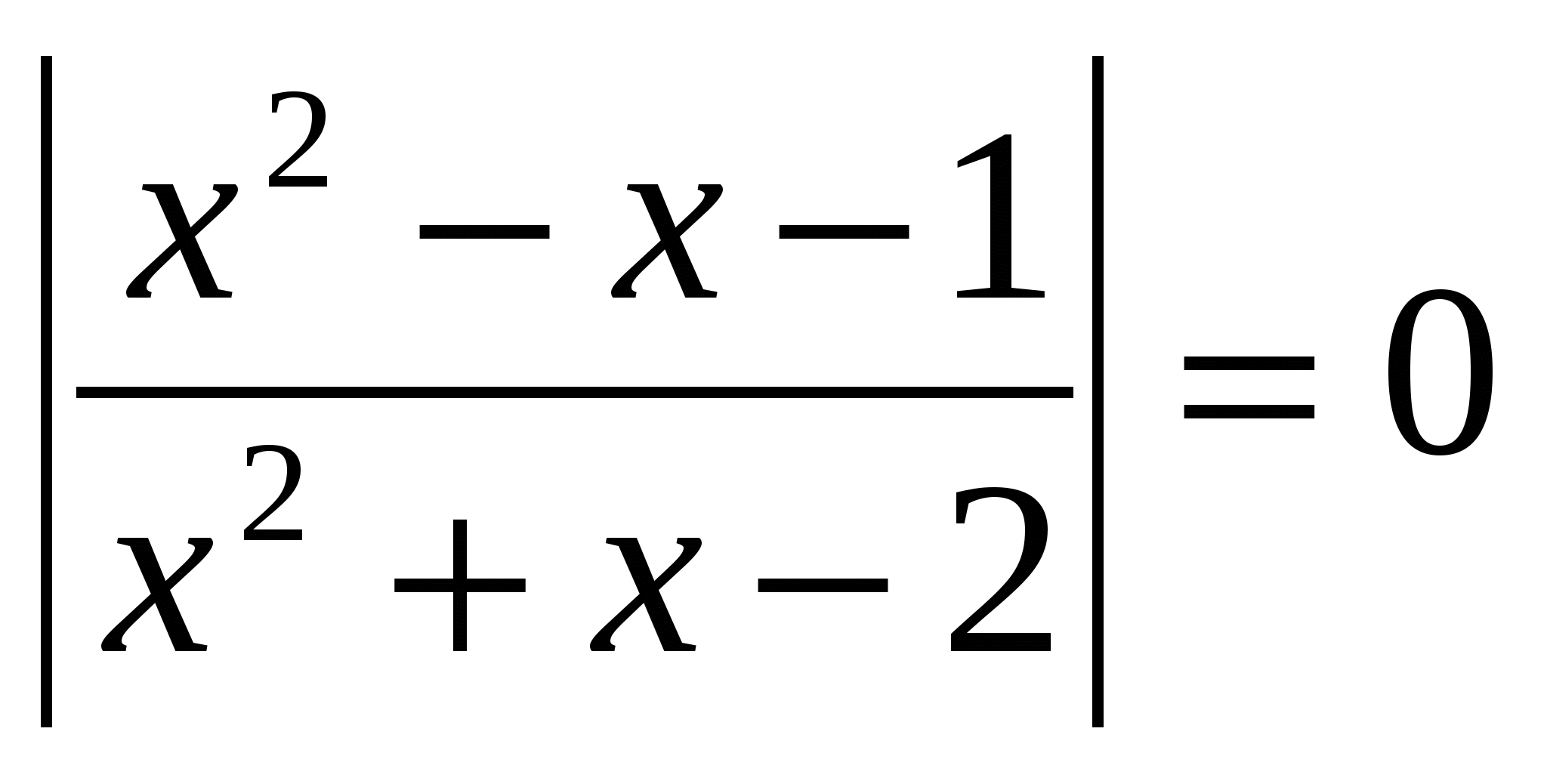 O.D.Z.
O.D.Z. 
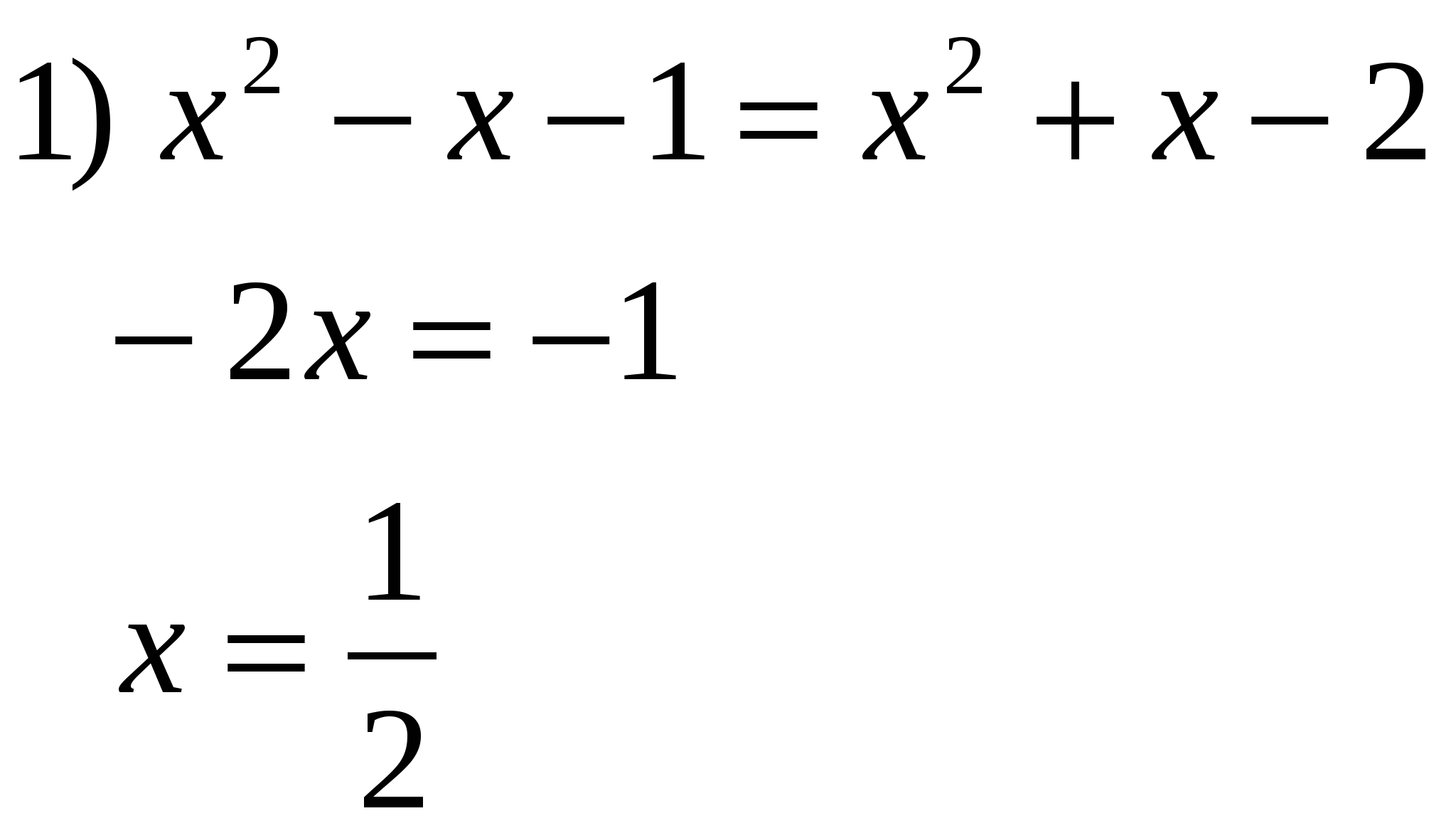
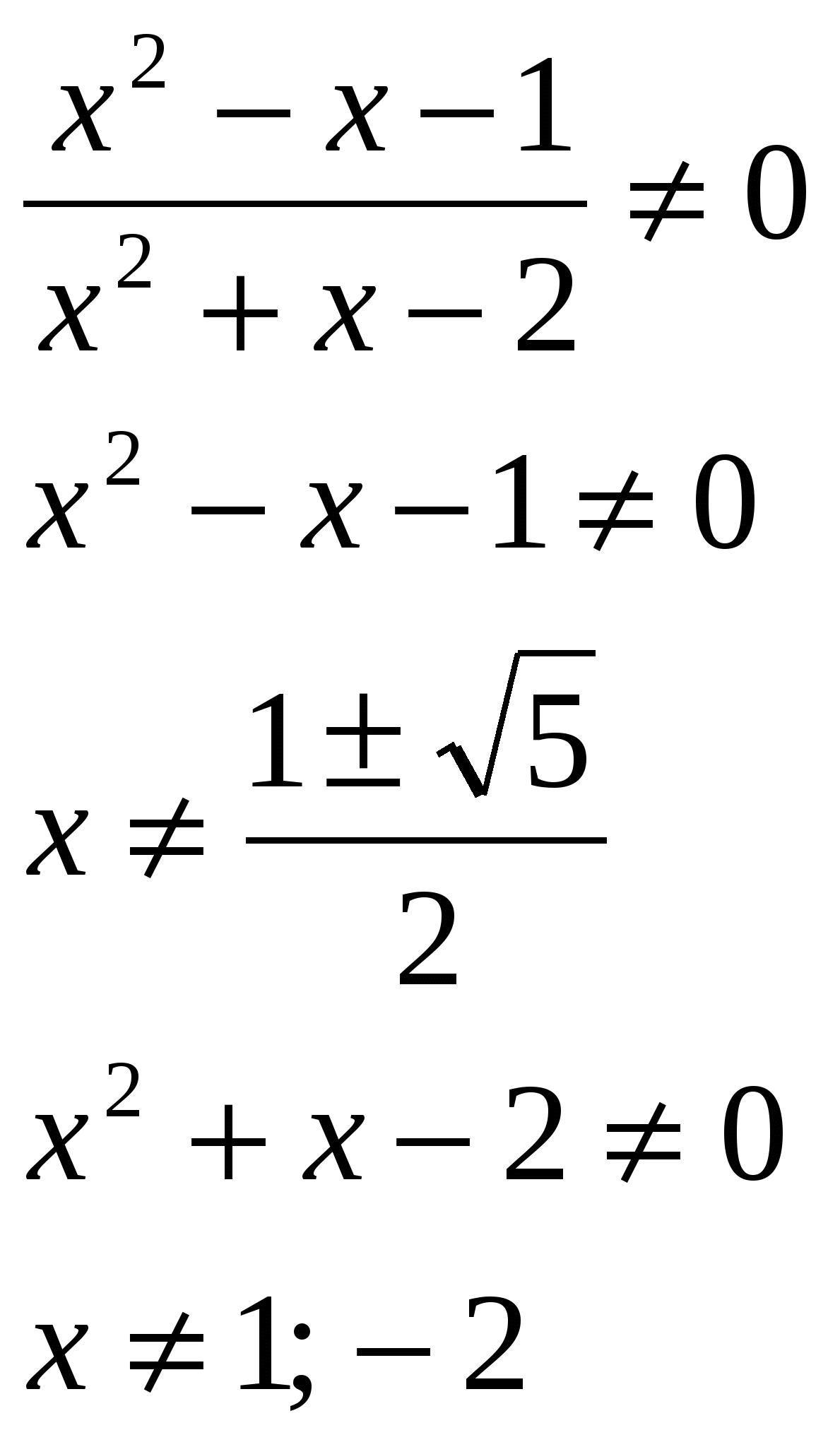

Verdict: the sum of roots is 0.5.
№3.
Untie the line: log 5  O.D.Z.
O.D.Z. 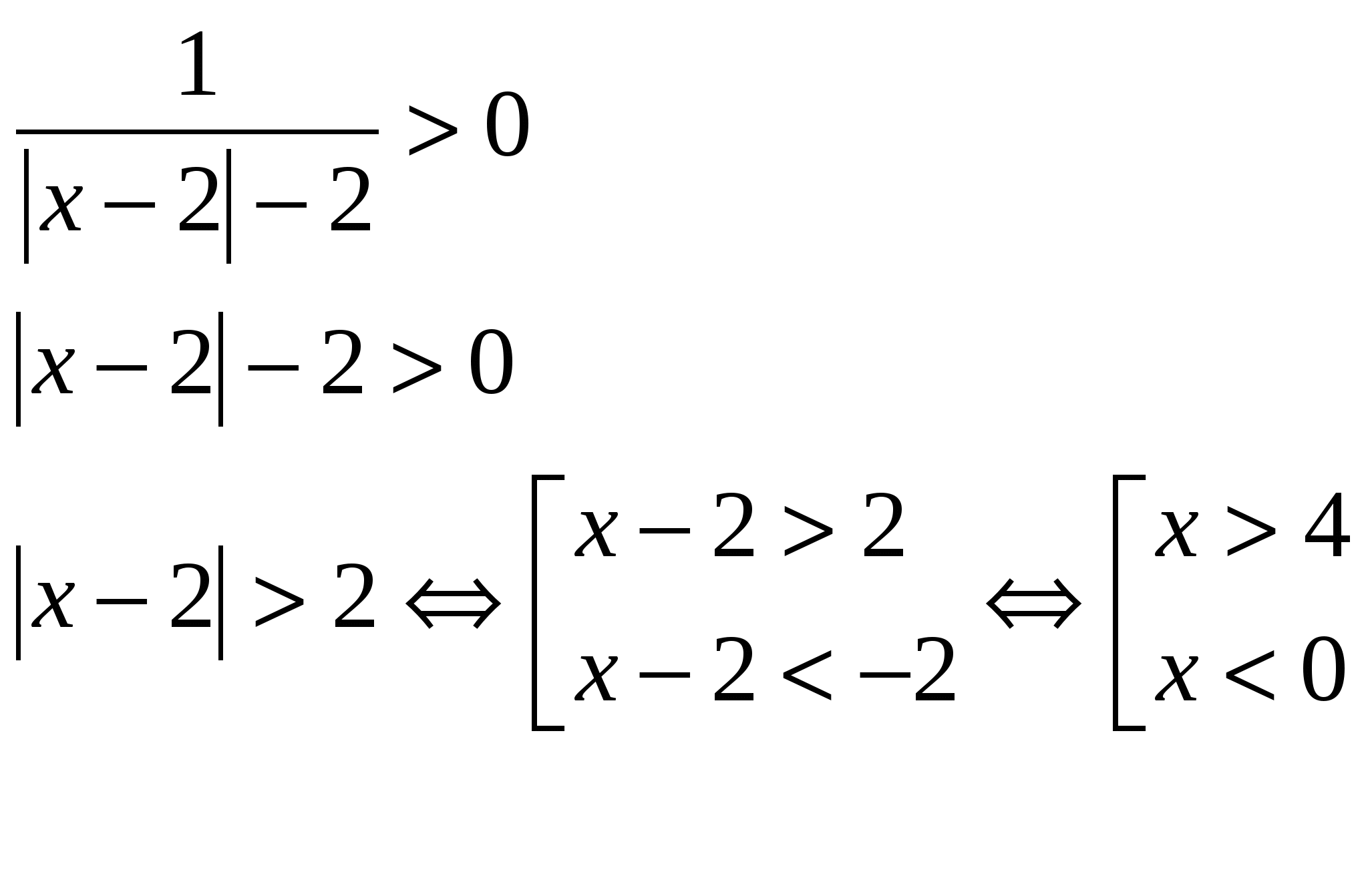
 Verdict: x = 9. №4.
Untie equalization: │2 + log 0.2 x│+ 3 = │1 + log 5 x│ O.D.Z. x > 0 Faster by the formula to the transition to the other basis. │2 - log 5 x│+ 3 = │1 + log 5 x│
Verdict: x = 9. №4.
Untie equalization: │2 + log 0.2 x│+ 3 = │1 + log 5 x│ O.D.Z. x > 0 Faster by the formula to the transition to the other basis. │2 - log 5 x│+ 3 = │1 + log 5 x│
│2 - log 5 x│- │1 + log 5 x│= - 3 We know zero submodular viruses: x = 25; x = qi numbers divide the range of admissible values by three intervals, which is equal to the sum of the three systems.  Suggestion: )
Suggestion: )